Protein hydrogen exchange at residue resolution by proteolytic fragmentation mass spectrometry analysis
- PMID: 24019478
- PMCID: PMC3799349
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1315532110
Protein hydrogen exchange at residue resolution by proteolytic fragmentation mass spectrometry analysis
Abstract
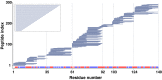
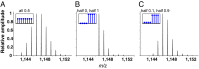
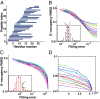
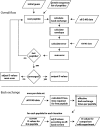
Hydrogen exchange technology provides a uniquely powerful instrument for measuring protein structural and biophysical properties, quantitatively and in a nonperturbing way, and determining how these properties are implemented to produce protein function. A developing hydrogen exchange-mass spectrometry method (HX MS) is able to analyze large biologically important protein systems while requiring only minuscule amounts of experimental material. The major remaining deficiency of the HX MS method is the inability to deconvolve HX results to individual amino acid residue resolution. To pursue this goal we used an iterative optimization program (HDsite) that integrates recent progress in multiple peptide acquisition together with previously unexamined isotopic envelope-shape information and a site-resolved back-exchange correction. To test this approach, residue-resolved HX rates computed from HX MS data were compared with extensive HX NMR measurements, and analogous comparisons were made in simulation trials. These tests found excellent agreement and revealed the important computational determinants.
Keywords: HDX-MS; isotope pattern; protein biophysics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Connelly GP, Bai Y, Jeng MF, Englander SW. Isotope effects in peptide group hydrogen exchange. Proteins. 1993;17(1):87–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

