Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL
- PMID: 24019532
- PMCID: PMC3829437
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462341
Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL
Abstract
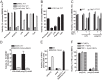
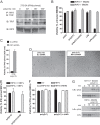
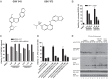
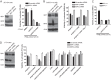
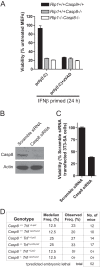
Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling is triggered by pathogen-associated molecular patterns that mediate well established cytokine-driven pathways, activating NF-κB together with IRF3/IRF7. In addition, TLR3 drives caspase 8-regulated programmed cell death pathways reminiscent of TNF family death receptor signaling. We find that inhibition or elimination of caspase 8 during stimulation of TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, or TLR9 results in receptor interacting protein (RIP) 3 kinase-dependent programmed necrosis that occurs through either TIR domain-containing adapter-inducing interferon-β (TRIF) or MyD88 signal transduction. TLR3 or TLR4 directly activates programmed necrosis through a RIP homotypic interaction motif-dependent association of TRIF with RIP3 kinase (also called RIPK3). In fibroblasts, this pathway proceeds independent of RIP1 or its kinase activity, but it remains dependent on mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) downstream of RIP3 kinase. Here, we describe two small molecule RIP3 kinase inhibitors and employ them to demonstrate the common requirement for RIP3 kinase in programmed necrosis induced by RIP1-RIP3, DAI-RIP3, and TRIF-RIP3 complexes. Cell fate decisions following TLR signaling parallel death receptor signaling and rely on caspase 8 to suppress RIP3-dependent programmed necrosis whether initiated directly by a TRIF-RIP3-MLKL pathway or indirectly via TNF activation and the RIP1-RIP3-MLKL necroptosis pathway.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Caspase; Necrosis (Necrotic Death); RIPK3; Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase; Toll-like Receptors (TLR).
Figures

References
-
- Lamkanfi M., Dixit V. M. (2010) Manipulation of host cell death pathways during microbial infections. Cell Host Microbe 8, 44–54 - PubMed
-
- Everett H., McFadden G. (1999) Apoptosis: an innate immune response to virus infection. Trends Microbiol. 7, 160–165 - PubMed
-
- Kumar H., Kawai T., Akira S. (2011) Pathogen recognition by the innate immune system. Int. Rev. Immunol. 30, 16–34 - PubMed
-
- Kaiser W. J., Offermann M. K. (2005) Apoptosis induced by the toll-like receptor adapter TRIF is dependent on its receptor interacting protein homotypic interaction motif. J. Immunol. 174, 4942–4952 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

