Effect of Zidovudine and its interaction with rocuronium on neuromuscular transmission
- PMID: 24019568
- PMCID: PMC3757858
Effect of Zidovudine and its interaction with rocuronium on neuromuscular transmission
Abstract
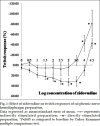
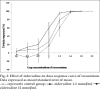
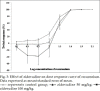
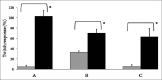
Neuromuscular weakness is often found in patients receiving zidovudine therapy due to mitochondrial damage. Effect of zidovudine was evaluated in indirectly and directly stimulated isolated rat phrenic nerve hemidiaphragm preparations, by cumulative dose response curve with square wave pulses, 0.5 ms duration of 2 Hz at every 10 s. To understand the observed effect of zidovudine, interaction studies were carried out with rocuronium. Dose response curve of rocuronium was compared in the absence and in the presence of 1.2 and 12 mmol/ml zidovudine. In another set of experiment, intact animals were treated with zidovudine 50 and 100 mg/kg for 15 days and phrenic nerve hemidiaphragm was obtained for in vitro experiment. Effect of zidovudine (30 mmol/ml) on twitch responses inhibited by dantrolene 50 μmol/ml, magnesium chloride 8 mmol/ml, rocuronium 10 μmol/ml, succinylcholine 25 μmol/ml and lignocaine 600 μmol/ml was studied. Zidovudine (3-30 mmol/ml) significantly augmented the twitch responses up to 80 and 40% in indirectly and directly stimulated preparations, respectively (P<0.05). Zidovudine did not show significant interaction with rocuronium in any group as per dose response curve and inhibitory concentration 5%, inhibitory concentration 50% and inhibitory concentration 95% of rocuronium. Zidovudine (30 mmol/ml) augmented the twitch responses inhibited by dantrolene, magnesium chloride and rocuronium. It reduced the time for complete block of succinylcholine (P<0.05). Zidovudine affects the neuromuscular transmission. No conclusive interaction between rocuronium and zidovudine was found.
Keywords: Drug interaction; neuromuscular transmission; rocuronium; zidovudine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuromuscular blocking effect of fluoxetine and its interaction with rocuronium.Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;33(1-2):17-24. doi: 10.1111/aap.12005. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Auton Autacoid Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23461555
-
Effects of magnesium chloride on rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade and sugammadex reversal in an isolated rat phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparation: An in-vitro study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018 Mar;35(3):193-199. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000714. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 28937530
-
The effect of phenytoin on rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block in the rat phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm preparation.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005 Jul;17(3):149-52. doi: 10.1097/01.ana.0000171732.18138.ce. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2005. PMID: 16037736
-
Dexamethasone concentration affecting rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade and sugammadex reversal in a rat phrenic nerve-hemidiaphragm model: An ex vivo study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018 Nov;35(11):856-862. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000866. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 30045055
-
In vitro neuromuscular effects of valproic acid.Br J Anaesth. 1997 Feb;78(2):197-200. doi: 10.1093/bja/78.2.197. Br J Anaesth. 1997. PMID: 9068341
References
-
- Dalakas MC, Illa I, Pezeshkpour GH, Laukaitis JP, Cohen B, Griffin JL. Mitochondrial myopathy caused by long-term zidovudine therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:1098–105. - PubMed
-
- Cazzalini O, Lazzè MC, Iamele L, Stivala LA, Bianchi L, Vaghi P, et al. Early effects of AZT on mitochondrial functions in the absence of mitochondrial DNA depletion in rat myotubes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2001;62:893–902. - PubMed
-
- Lewis W. Mitochondrial dysfunction and nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor therapy: Experimental clarifications and persistent clinical questions. Antiviral Res. 2003;58:189–97. - PubMed
-
- Scruggs ER, Dirks Naylor AJ. Mechanisms of zidovudine-induced mitochondrial toxicity and myopathy. Pharmacology. 2008;82:83–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
