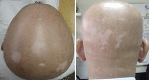
Diphenylcyclopropenone-induced vitiligo in a patient with alopecia universalis
- PMID: 24019775
- PMCID: PMC3764942
- DOI: 10.1159/000354767
Diphenylcyclopropenone-induced vitiligo in a patient with alopecia universalis
Abstract
Alopecia areata and vitiligo are autoimmune diseases, both associated with multiple autoimmune comorbidities. Many studies show colocalization of these diseases at the same anatomical site. Here, we have a case where both disorders were reported to present in the same patient. Diphenylcyclopropenone (diphencyprone, DCP) is used in the treatment of alopecia areata and may induce vitiligo in some patients. We report on one case of vitiligo that was induced by DCP during therapy for alopecia universalis. Alopecia areata and vitiligo share many susceptibility genes. Follicular melanocyte destruction may represent the link between the two diseases.
Keywords: Alopecia; Diphenylcyclopropenone; Vitiligo.
Figures
References
-
- Hordinsky M, Ericson M. Autoimmunity: alopecia areata. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc. 2004;9:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Krüger C, Schallreuter KU. A review of the worldwide prevalence of vitiligo in children/adolescents and adults. Int J Dermatol. 2012;51:1206–1212. - PubMed
-
- Dhar S, Kanwar AJ. Colocalization of vitiligo and alopecia areata. Pediatr Dermatol. 1994;11:85–86. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous