Quantitative structure activities relationships of some 2-mercaptoimidazoles as CCR2 inhibitors using genetic algorithm-artificial neural networks
- PMID: 24019819
- PMCID: PMC3764681
Quantitative structure activities relationships of some 2-mercaptoimidazoles as CCR2 inhibitors using genetic algorithm-artificial neural networks
Abstract
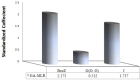
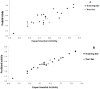
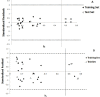
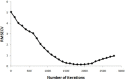
Quantitative relationships between structures of twenty six of 2-mercaptoimidazoles as C-C chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2) inhibitors were assessed. Modeling of the biological activities of compounds of interest as a function of molecular structures was established by means of genetic algorithm multivariate linear regression (GA-MLR) and genetic algorithm (GA-ANN). The results showed that, the pIC50 values calculated by GA-ANN are in good agreement with the experimental data, and the performance of the artificial neural networks regression model is superior to the multivariate linear regression-based (MLR) model. With respect to the obtained results, it can be deduced that there is a non-linear relationship between the pIC50 s and the calculated structural descriptors of the 2-mercaptoimidazoles. The obtained models were able to describe about 78% and 93% of the variance in the experimental activity of molecules in training set, respectively. The study provided a novel and effective approach for predicting biological activities of 2-mercaptoimidazole derivatives as CCR2 inhibitors and disclosed that combined genetic algorithm and GA-ANN can be used as a powerful chemometric tools for quantitative structure activity relationship (QSAR) studies.
Keywords: 2-mercaptoimidazoles; Artificial neural networks; CCR2 inhibitors; Multivariate linear regression; Quantitative structure activity relationship.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Application of GA-MLR for QSAR Modeling of the Arylthioindole Class of Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(4):552-565. doi: 10.2174/1871520616666160811162105. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27528182
-
Rational Design of a Low-Data Regime of Pyrrole Antioxidants for Radical Scavenging Activities Using Quantum Chemical Descriptors and QSAR with the GA-MLR and ANN Concepts.Molecules. 2023 Feb 7;28(4):1596. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041596. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838583 Free PMC article.
-
QSAR analysis for some diaryl-substituted pyrazoles as CCR2 inhibitors by GA-stepwise MLR.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011 Jan;77(1):75-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0285.2010.01053.x. Epub 2010 Nov 30. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011. PMID: 21118376
-
QSAR modeling for quinoxaline derivatives using genetic algorithm and simulated annealing based feature selection.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(30):4032-48. doi: 10.2174/092986709789352303. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747124 Review.
-
Genetic algorithm optimization in drug design QSAR: Bayesian-regularized genetic neural networks (BRGNN) and genetic algorithm-optimized support vectors machines (GA-SVM).Mol Divers. 2011 Feb;15(1):269-89. doi: 10.1007/s11030-010-9234-9. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Mol Divers. 2011. PMID: 20306130 Review.
Cited by
-
Rational design of novel coumarins: A potential trend for antioxidants in cosmetics.EXCLI J. 2020 Feb 26;19:209-226. doi: 10.17179/excli2019-1903. eCollection 2020. EXCLI J. 2020. PMID: 32256267 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative structure-activity relationship study of P2X7 receptor inhibitors using combination of principal component analysis and artificial intelligence methods.Res Pharm Sci. 2015 Jul-Aug;10(4):307-25. Res Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26600858 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum to: Does being an Olympic city help improve recreational resources? Examining the quality of physical activity resources in a low-income neighborhood of Rio de Janeiro.Int J Public Health. 2017 Mar;62(2):269-270. doi: 10.1007/s00038-016-0869-x. Int J Public Health. 2017. PMID: 27628487 No abstract available.
-
QSAR analysis of pyrimidine derivatives as VEGFR-2 receptor inhibitors to inhibit cancer using multiple linear regression and artificial neural network.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 Oct 15;16(6):596-611. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.327506. eCollection 2021 Dec. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34760008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feria M, Diaz-Gonzalez F. The CCR2 receptor as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2006;16:49–57.
-
- Bachmann MF, Kopf M, Marsland BJ. Chemokines: more than just road signs. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6:159–164. - PubMed
-
- Carter PH. Chemokine receptor antagonism as an approach to anti-inflammatory therapy: ’just right’ or plain wrong? Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2002:6510–6525. - PubMed
-
- Gao Z, Metz WA. Unraveling the chemistry of chemokine receptor ligands. Chem Rev. 2003;103:3733–3752. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz MK, Wells TN. New therapeutics that modulate chemokine networks. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2002;1:347–358. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
