Quantitative evaluation of DNMT3B promoter methylation in breast cancer patients using differential high resolution melting analysis
- PMID: 24019826
- PMCID: PMC3764668
Quantitative evaluation of DNMT3B promoter methylation in breast cancer patients using differential high resolution melting analysis
Abstract
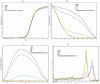
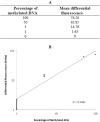
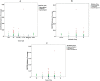
DNA methylation plays an important role in carcinogenesis through epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes. Aberrant methylation usually results from changes in the activity of DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). Some studies show that the overexpression of the DNMTs may lead to aberrant methylation of tumor suppressor genes. Also the overexpression of DNMTs may be related to methylation status of their genes. Due to limited number of studies on DNMT3B promoter methylation, this study was performed to quantitatively measure the methylation level of DNMT3B gene in archival formalin fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues from breast cancer patients. Using differential high resolution melting analysis (D-HRMA) technology, the methylation level of DNMT3B gene promoter was quantified in 98 breast cancer FFPE tissues and also 10 fresh frozen normal tissue samples. Statistical analyses used for analyzing the correlation between the methylation and clinical variables. All the normal samples were found to be methylated at the DNMT3B promoter (the average methylation level 3.34%). Patients were identified as hypo-methylated (mean methylation level 0.8%), methylated (mean methylation level 2.48%) and hyper-methylated (mean methylation level 10.5%). Statistical analysis showed a significant correlation between the methylation status and the sample type, cancer type and tumor size. Also the methylation level was significantly associated with histologic grade. It is concluded that quantification of DNMT3B promoter methylation might be used as a reliable and sensitive diagnostic and prognostic tool in breast cancer. Also D-HRMA is demonstrated as a rapid and cost effective method for quantitative evaluation of promoter methylation.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DNA methylation; DNMT3B; FFPE; High resolution melting analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitation of CDH1 promoter methylation in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of breast cancer patients using differential high resolution melting analysis.Adv Biomed Res. 2016 May 30;5:91. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.183139. eCollection 2016. Adv Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 27308263 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Role of siRNA Mediated Promoter Methylation in DNMT3B Knockdown and Alteration of Promoter Methylation of CDH1, GSTP1 Genes in MDA-MB -453 Cell Line.Iran J Pharm Res. 2017 Spring;16(2):771-780. Iran J Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28979331 Free PMC article.
-
Altered DNA methyltransferases promoter methylation and mRNA expression are associated with tamoxifen response in breast tumors.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):7305-7319. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26562. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29574992
-
A rapid and accurate closed-tube Methylation-Sensitive High Resolution Melting Analysis assay for the semi-quantitative determination of SOX17 promoter methylation in clinical samples.Clin Chim Acta. 2015 Apr 15;444:303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.02.035. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Clin Chim Acta. 2015. PMID: 25727515
-
Epigenetic regulation of DNA methyltransferases: DNMT1 and DNMT3B in gliomas.J Neurooncol. 2011 Sep;104(2):483-94. doi: 10.1007/s11060-010-0520-2. Epub 2011 Jan 13. J Neurooncol. 2011. PMID: 21229291
Cited by
-
The effect of valproic acid on intrinsic, extrinsic, and JAK/STAT pathways in neuroblastoma and glioblastoma cell lines.Res Pharm Sci. 2022 Jul 14;17(4):392-409. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.350240. eCollection 2022 Aug. Res Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 36034083 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of promoter methylation patterns association with genes expression profile of ISL1, MGMT and DMNT3b in tissue of breast cancer patients.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Feb;49(2):847-857. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06546-z. Epub 2022 Jan 8. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34997427
-
Comparison of the effects of olsalazine and decitabine on the expression of CDH1 and uPA genes and cytotoxicity in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 May 12;16(3):278-285. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.314826. eCollection 2021 Jun. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34221061 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of CDH1 promoter methylation in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of breast cancer patients using differential high resolution melting analysis.Adv Biomed Res. 2016 May 30;5:91. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.183139. eCollection 2016. Adv Biomed Res. 2016. PMID: 27308263 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the Role of siRNA Mediated Promoter Methylation in DNMT3B Knockdown and Alteration of Promoter Methylation of CDH1, GSTP1 Genes in MDA-MB -453 Cell Line.Iran J Pharm Res. 2017 Spring;16(2):771-780. Iran J Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28979331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lin RK, Hsu HS, Chang JW, Chen CY, Chen JT, Wang YC. Alteration of DNA methyltransferses contributes to 5’CpG methylation and poor prognosis in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2007;55:205–213. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
