Synthesis, analysis and cytotoxic evaluation of some hydroxypyridinone derivatives on HeLa and K562 cell lines
- PMID: 24019828
- PMCID: PMC3764670
Synthesis, analysis and cytotoxic evaluation of some hydroxypyridinone derivatives on HeLa and K562 cell lines
Abstract
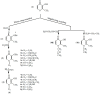
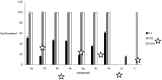
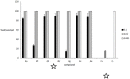
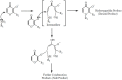
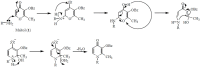
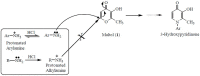
A range of iron bidentae ligands containing the chelating moiety 3- hydroxypyridin-4-ones (HPOs) have been synthesized via a single or a three-step synthetic pathway. In the single-step reaction, maltol was directly reacted by suitable primary amine and in the second synthetic method; benzylated maltol was reacted with related amines to give 1-substuted-2-methyl-3-benzyloxypyridin-4-one derivatives. Finally, removal of the benzyl group under acidic conditions was performed by catalytic hydrogenation to yield the favored bidentate chelators as HCl salt. The partition coefficient of the free ligands and their iron (III) complexes between an aqueous phase buffered at pH 7.4 and 1-octanol were also determined. The cytotoxic effects of these iron chelators against HeLa and K562 cell lines were evaluated using MTT assay and the results showed that cytotoxicity was closely related to the lipophilicity of compounds so that the most lipophilic compound (4g) revealed the highest activity and compound 4e as a more hydrophilic agent (Kpart; 0.05) showed the lowest cytotoxic effect.
Keywords: 3-Hydroxypyridin-4-ones; Cytotoxicity; HeLa and K562 cells; Iron chelating agents; Lipophilicity.
Figures
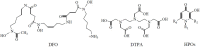
References
-
- Crichton RR, Ward RJ. Iron metabolism-new perspectives in view. Biochemistry. 1992;31:11255–11264. - PubMed
-
- Toyokuni S. Iron-induced carcinogenesis: the role of redox regulation. Free Radical Biol Med. 1996;20:553–566. - PubMed
-
- Weinberg ED. Iron, asbestos, and carcinogenicity. Lancet. 1989;1:1399–1400. - PubMed
-
- Green DA, Antholine WE, Wong SJ, Richardson DR, Chitambar CR. Inhibition of malignant cell growth by 311, a novel iron chelator of the pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone class: effect on the R2 subunit of ribonucleotide reductase. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3574–3579. - PubMed
-
- Fukuchi K, Tomoyasu S, Tsuruoka N, Gomi K. Iron deprivation-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1994;350:139–142. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
