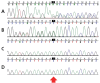
A novel MLL2 gene mutation in a Korean patient with Kabuki syndrome
- PMID: 24019847
- PMCID: PMC3764261
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2013.56.8.355
A novel MLL2 gene mutation in a Korean patient with Kabuki syndrome
Abstract
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disease with a distinctive dysmorphic face, intellectual disability, and multiple congenital abnormalities. KS is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. As the primary cause of KS, MLL2 mutations have been identified in 56-76% of affected individuals who have been tested, suggesting that there may be additional genes associated with KS. Recently, a few KS individuals have been found to have de novo partial or complete deletions of an X chromosome gene, KDM6A, which encodes a histone demethylase that interacts with MLL2. Nevertheless, mutations in MLL2 are the major cause of KS. Although there are a few reports of KS patients in Korea, none of these had been confirmed by genetic analysis. Here, we report a case of a Korean patient with clinical features of KS. Using direct sequencing, we identified a frameshift heterozygous mutation for MLL2: (c.5256_5257delGA;p.Lys1753Alafs*34). Clinically, the patient presented with typical facial features, and diagnosis of KS was based on the diagnostic criteria. While KS is a rare disease, other malformations that overlap with those found in individuals with KS are common. Hence, the diagnosis of KS by mutational analysis can be a valuable method for patients with KS-like syndromes. Furthermore, in the near future, other genes could be identified in patients with KS without a detectable MLL2 mutation.
Keywords: KDM6; KS-associated genes; Kabuki syndrome; MLL2 mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deletion of KDM6A, a histone demethylase interacting with MLL2, in three patients with Kabuki syndrome.Am J Hum Genet. 2012 Jan 13;90(1):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.11.021. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Am J Hum Genet. 2012. PMID: 22197486 Free PMC article.
-
MLL2 mutation spectrum in 45 patients with Kabuki syndrome.Hum Mutat. 2011 Feb;32(2):E2018-25. doi: 10.1002/humu.21416. Epub 2010 Dec 7. Hum Mutat. 2011. PMID: 21280141
-
Mutation Update for Kabuki Syndrome Genes KMT2D and KDM6A and Further Delineation of X-Linked Kabuki Syndrome Subtype 2.Hum Mutat. 2016 Sep;37(9):847-64. doi: 10.1002/humu.23026. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Hum Mutat. 2016. PMID: 27302555
-
Unraveling molecular pathways shared by Kabuki and Kabuki-like syndromes.Clin Genet. 2018 Oct;94(3-4):283-295. doi: 10.1111/cge.12983. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Clin Genet. 2018. PMID: 28139835 Review.
-
Kabuki syndrome: clinical and molecular diagnosis in the first year of life.Arch Dis Child. 2015 Feb;100(2):158-64. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-305858. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Arch Dis Child. 2015. PMID: 25281733 Review.
Cited by
-
Facial Dysmorphisms, Macrodontia, Focal Epilepsy, and Thinning of the Corpus Callosum: A Rare Mild Form of Kabuki Syndrome.J Pediatr Genet. 2021 Mar;10(1):49-52. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1701645. Epub 2020 Feb 17. J Pediatr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33552639 Free PMC article.
-
Kabuki syndrome: clinical and molecular characteristics.Korean J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;58(9):317-24. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2015.58.9.317. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Korean J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26512256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of KMT2D and KDM6A mutations by exome sequencing in Korean patients with Kabuki syndrome.J Hum Genet. 2014 Jun;59(6):321-5. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2014.25. Epub 2014 Apr 17. J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24739679
-
A novel KMT2D mutation resulting in Kabuki syndrome: A case report.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3641-5. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5683. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27573763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niikawa N, Matsuura N, Fukushima Y, Ohsawa T, Kajii T. Kabuki make-up syndrome: a syndrome of mental retardation, unusual facies, large and protruding ears, and postnatal growth deficiency. J Pediatr. 1981;99:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y, Suzuki Y, Chyo H, Hata A, Matsui I. A new malformation syndrome of long palpebral fissures, large ears, depressed nasal tip, and skeletal anomalies associated with postnatal dwarfism and mental retardation. J Pediatr. 1981;99:570–573. - PubMed
-
- Niikawa N, Kuroki Y, Kajii T, Matsuura N, Ishikiriyama S, Tonoki H, et al. Kabuki make-up (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome: a study of 62 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:565–589. - PubMed
-
- Park SK, Park DK, Choung JT, Son CS, Dokgo YC. A case of Kabuki make-up syndrome. J Korean Med Assoc. 1991;34:790–792.
-
- Huh JK, Chung MS, Baek GH, Oh JH, Lee YH, Gong HS. Cleft hand in Kabuki make-up syndrome: case report. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36:653–657. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous