Genome of the R-body producing marine alphaproteobacterium Labrenzia alexandrii type strain (DFL-11(T))
- PMID: 24019989
- PMCID: PMC3764935
- DOI: 10.4056/sigs.3456959
Genome of the R-body producing marine alphaproteobacterium Labrenzia alexandrii type strain (DFL-11(T))
Abstract
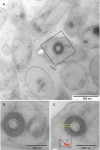
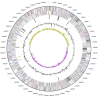
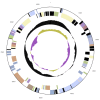
Labrenzia alexandrii Biebl et al. 2007 is a marine member of the family Rhodobacteraceae in the order Rhodobacterales, which has thus far only partially been characterized at the genome level. The bacterium is of interest because it lives in close association with the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium lusitanicum. Ultrastructural analysis reveals R-bodies within the bacterial cells, which are primarily known from obligate endosymbionts that trigger "killing traits" in ciliates (Paramecium spp.). Genomic traits of L. alexandrii DFL-11(T) are in accordance with these findings, as they include the reb genes putatively involved in R-body synthesis. Analysis of the two extrachromosomal elements suggests a role in heavy-metal resistance and exopolysaccharide formation, respectively. The 5,461,856 bp long genome with its 5,071 protein-coding and 73 RNA genes consists of one chromosome and two plasmids, and has been sequenced in the context of the Marine Microbial Initiative.
Keywords: Alexandrium lusitanicum; Alphaproteobacteria; aerobe; dinoflagellates; high-quality draft; motile; photoheterotroph; symbiosis.
Figures


References
-
- Biebl H, Pukall R, Lünsdorf H, Schulz S, Allgaier M, Tindall BJ, Wagner-Döbler I. Description of Labrenzia alexandrii gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel alphaproteobacterium containing bacteriochlorophyll a, and a proposal for reclassification of Stappia aggregata as Labrenzia aggregata comb. nov., of Stappia marina as Labrenzia marina comb. nov. and of Stappia alba as Labrenzia alba comb. nov., and emended descriptions of the genera Pannonibacter, Stappia and Roseibium, and of the species Roseibium denhamense and Roseibium hamelinense. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2007; 57:1095-1107 10.1099/ijs.0.64821-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garrity GM, Bell JA, Lilburn T. Order III. Rhodobacteraceae fam. nov. In: Garrity GM, Brenner DJ, Krieg NR, Staley JT (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Second Edition, Volume 2, Part C, Springer, New York, 2005, p. 161. - DOI
-
- Lee KB, Liu CT, Anzai Y, Kim H, Aono T, Oyaizu H. The hierarchical system of the ‘Alphaproteobacteria’: description of Hyphomonadaceae fam. nov., Xanthobacteraceae fam. nov. and Erythrobacteraceae fam. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2005; 55:1907-1919 10.1099/ijs.0.63663-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 1990; 215:403-410 - PubMed
-
- Korf I, Yandell M, Bedell J. BLAST, O'Reilly, Sebastopol, 2003.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

