Sequence selectivity of the cleavage sites induced by topoisomerase I inhibitors: a molecular dynamics study
- PMID: 24021629
- PMCID: PMC3905861
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt791
Sequence selectivity of the cleavage sites induced by topoisomerase I inhibitors: a molecular dynamics study
Abstract
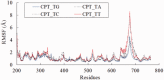
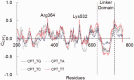
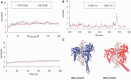
Topoisomerase IB (Top1) inhibitors, such as camptothecin (CPT), stabilize the Top1-DNA cleavage complex in a DNA sequence-dependent manner. The sequence selectivity of Top1 inhibitors is important for targeting specific genomic sequences of therapeutic value. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying this selectivity remain largely unknown. We performed molecular dynamics simulations to delineate structural, dynamic and energetic features that contribute to the differential sequence selectivity of the Top1 inhibitors. We found the sequence selectivity of CPT to be highly correlated with the drug binding energies, dynamic and structural properties of the linker domain. Chemical insights, gained by per-residue binding energy analysis revealed that the non-polar interaction between CPT and nucleotide at the +1 position of the cleavage site was the major (favorable) contributor to the total binding energy. Mechanistic insights gained by a potential of mean force analysis implicated that the drug dissociation step was associated with the sequence selectivity. Pharmaceutical insights gained by our molecular dynamics analyses explained why LMP-776, an indenoisoquinoline derivative under clinical development at the National Institutes of Health, displays different sequence selectivity when compared with camptothecin and its clinical derivatives.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Role of the protein in the DNA sequence specificity of the cleavage site stabilized by the camptothecin topoisomerase IB inhibitor: a metadynamics study.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Dec;41(22):9977-86. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt790. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 24003027 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of two models for human topoisomerase I interaction with dsDNA and camptothecin derivatives.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024314. Epub 2011 Aug 30. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21912628 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular modeling studies of the DNA-topoisomerase I ternary cleavable complex with camptothecin.J Med Chem. 1998 Jun 18;41(13):2216-26. doi: 10.1021/jm9605445. J Med Chem. 1998. PMID: 9632354
-
Topoisomerase I inhibitors: Challenges, progress and the road ahead.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Jun 5;236:114304. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114304. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35413618 Review.
-
Camptothecins as probes of the microenvironments of topoisomerase I--DNA complexes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;922:76-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb07027.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000. PMID: 11193927 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular basis for the DNA damage induction and anticancer activity of asymmetrically substituted anthrapyridazone PDZ-7.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 10;8(62):105137-105154. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21806. eCollection 2017 Dec 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29285240 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase IB: a relaxing enzyme for stressed DNA.Cancer Drug Resist. 2020 Mar 19;3(1):18-25. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2019.106. eCollection 2020. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 35582040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Functional Consequences of Eukaryotic Topoisomerase 1 Interaction with G-Quadruplex DNA.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 12;11(2):193. doi: 10.3390/genes11020193. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32059547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CFS-1686 causes cell cycle arrest at intra-S phase by interference of interaction of topoisomerase 1 with DNA.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e113832. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113832. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25460368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antony S, Agama KK, Miao ZH, Takagi K, Wright MH, Robles AI, Varticovski L, Nagarajan M, Morrell A, Cushman M, et al. Novel indenoisoquinolines NSC 725776 and NSC 724998 produce persistent topoisomerase I cleavage complexes and overcome multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 2007;67:10397–10405. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Zhou X, Hecht SM. Role of the 20-hydroxyl group in camptothecin binding by the topoisomerase I-DNA binary complex. Biochemistry. 1999;38:4374–4381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

