IL-27p28 inhibits central nervous system autoimmunity by concurrently antagonizing Th1 and Th17 responses
- PMID: 24021664
- PMCID: PMC3975693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2013.08.003
IL-27p28 inhibits central nervous system autoimmunity by concurrently antagonizing Th1 and Th17 responses
Abstract
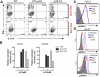
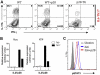
Central nervous system (CNS) autoimmunity such as uveitis and multiple sclerosis is accompanied by Th1 and Th17 responses. In their corresponding animal models, experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), both responses are induced and can drive disease independently. Because immune responses have inherent plasticity, therapeutic targeting of only one pathway could promote the other, without reducing pathology. IL-27p28 antagonizes gp130, required for signaling by IL-27 and IL-6, which respectively promote Th1 and Th17 responses. We therefore examined its ability to protect the CNS by concurrently targeting both effector responses. Overexpression of IL-27p28 in vivo ameliorated EAU as well as EAE pathology and reduced tissue infiltration by Th1 and Th17 cells in a disease prevention, as well as in a disease reversal protocol. Mechanistic studies revealed inhibition of Th1 and Th17 commitment in vitro and decreased lineage stability of pre-formed effectors in vivo, with reduction in expression of gp130-dependent transcription factors and cytokines. Importantly, IL-27p28 inhibited polarization of human T cells to the Th1 and Th17 effector pathways. The ability of IL-27p28 to inhibit generation as well as function of pathogenic Th1 and Th17 effector cells has therapeutic implications for controlling immunologically complex autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; IL-27p28; gp130.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

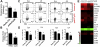
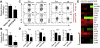

References
-
- Chi W, Yang P, Li B, Wu C, Jin H, Zhu X, et al. IL-23 promotes CD4+ T cells to produce IL-17 in Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:1218–24. - PubMed
-
- Amadi-Obi A, Yu CR, Liu X, Mahdi RM, Clarke GL, Nussenblatt RB, et al. TH17 cells contribute to uveitis and scleritis and are expanded by IL-2 and inhibited by IL-27/STAT1. Nat Med. 2007;13:711–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
