Cytosolic carboxypeptidase 5 removes α- and γ-linked glutamates from tubulin
- PMID: 24022482
- PMCID: PMC3798508
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.497917
Cytosolic carboxypeptidase 5 removes α- and γ-linked glutamates from tubulin
Abstract
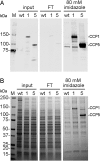
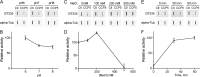
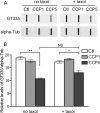
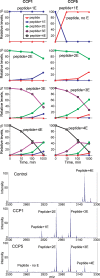
Cytosolic carboxypeptidase 5 (CCP5) is a member of a subfamily of enzymes that cleave C-terminal and/or side chain amino acids from tubulin. CCP5 was proposed to selectively cleave the branch point of glutamylated tubulin, based on studies involving overexpression of CCP5 in cell lines and detection of tubulin forms with antisera. In the present study, we examined the activity of purified CCP5 toward synthetic peptides as well as soluble α- and β-tubulin and paclitaxel-stabilized microtubules using a combination of antisera and mass spectrometry to detect the products. Mouse CCP5 removes multiple glutamate residues and the branch point glutamate from the side chains of porcine brain α- and β-tubulin. In addition, CCP5 excised C-terminal glutamates from detyrosinated α-tubulin. The enzyme also removed multiple glutamate residues from side chains and C termini of paclitaxel-stabilized microtubules. CCP5 both shortens and removes side chain glutamates from synthetic peptides corresponding to the C-terminal region of β3-tubulin, whereas cytosolic carboxypeptidase 1 shortens the side chain without cleaving the peptides' γ-linked residues. The rate of cleavage of α linkages by CCP5 is considerably slower than that of removal of a single γ-linked glutamate residue. Collectively, our data show that CCP5 functions as a dual-functional deglutamylase cleaving both α- and γ-linked glutamate from tubulin.
Keywords: Carboxypeptidase; Cytosolic Carboxypeptidase; Enzymes; Metalloenzymes; Peptidases; Tubulin.
Figures


References
-
- Gunawardena S., Her L. S., Brusch R. G., Laymon R. A., Niesman I. R., Gordesky-Gold B., Sintasath L., Bonini N. M., Goldstein L. S. (2003) Disruption of axonal transport by loss of huntingtin or expression of pathogenic polyQ proteins in Drosophila. Neuron 40, 25–40 - PubMed
-
- Sinadinos C., Burbidge-King T., Soh D., Thompson L. M., Marsh J. L., Wyttenbach A., Mudher A. K. (2009) Live axonal transport disruption by mutant huntingtin fragments in Drosophila motor neuron axons. Neurobiol. Dis. 34, 389–395 - PubMed
-
- Kanaan N. M., Morfini G. A., LaPointe N. E., Pigino G. F., Patterson K. R., Song Y., Andreadis A., Fu Y., Brady S. T., Binder L. I. (2011) Pathogenic forms of Tau inhibit kinesin-dependent axonal transport through a mechanism involving activation of axonal phosphotransferases. J. Neurosci. 31, 9858–9868 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

