How a CCA sequence protects mature tRNAs and tRNA precursors from action of the processing enzyme RNase BN/RNase Z
- PMID: 24022488
- PMCID: PMC3798534
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514570
How a CCA sequence protects mature tRNAs and tRNA precursors from action of the processing enzyme RNase BN/RNase Z
Abstract
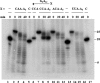
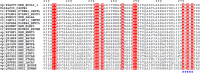
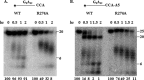
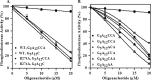
In many organisms, 3' maturation of tRNAs is catalyzed by the endoribonuclease, RNase BN/RNase Z, which cleaves after the discriminator nucleotide to generate a substrate for addition of the universal CCA sequence. However, tRNAs or tRNA precursors that already contain a CCA sequence are not cleaved, thereby avoiding a futile cycle of removal and readdition of these essential residues. We show here that the adjacent C residues of the CCA sequence and an Arg residue within a highly conserved sequence motif in the channel leading to the RNase catalytic site are both required for the protective effect of the CCA sequence. When both of these determinants are present, CCA-containing RNAs in the channel are unable to move into the catalytic site; however, substitution of either of the C residues by A or U or mutation of Arg(274) to Ala allows RNA movement and catalysis to proceed. These data define a novel mechanism for how tRNAs are protected against the promiscuous action of a processing enzyme.
Keywords: Enzyme Structure; Nucleic Acid Chemistry; Nucleic Acid Enzymology; Phosphodiesterases; Protein-Nucleic Acid Interaction; RNA Catalysis; RNA Processing; RNA-Protein Interaction; Structural Biology; Transfer RNA (tRNA).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mode of action of RNase BN/RNase Z on tRNA precursors: RNase BN does not remove the CCA sequence from tRNA.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 23;285(30):22874-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.141101. Epub 2010 May 19. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20489203 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of the 3'-end of tRNA with ribonuclease P RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4087-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4087. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994. PMID: 7524035 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic properties of RNase BN/RNase Z from Escherichia coli: RNase BN is both an exo- and endoribonuclease.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jun 5;284(23):15425-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.005462. Epub 2009 Apr 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19366704 Free PMC article.
-
A tRNA's fate is decided at its 3' end: Collaborative actions of CCA-adding enzyme and RNases involved in tRNA processing and degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018 Apr;1861(4):433-441. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.01.012. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018. PMID: 29374586 Review.
-
RNase P from bacteria. Substrate recognition and function of the protein subunit.Mol Biol Rep. 1995-1996;22(2-3):99-109. doi: 10.1007/BF00988713. Mol Biol Rep. 1995. PMID: 8901495 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial poly(A) polymerase is involved in tRNA repair.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Nov 16;43(20):9937-49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv891. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26354863 Free PMC article.
-
Critical Minireview: The Fate of tRNACys during Oxidative Stress in Bacillus subtilis.Biomolecules. 2017 Jan 20;7(1):6. doi: 10.3390/biom7010006. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28117687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel mechanism of ribonuclease regulation: GcvB and Hfq stabilize the mRNA that encodes RNase BN/Z during exponential phase.J Biol Chem. 2019 Dec 27;294(52):19997-20008. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011367. Epub 2019 Nov 19. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31744883 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial ribonucleases and their roles in RNA metabolism.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 Jun;54(3):242-300. doi: 10.1080/10409238.2019.1651816. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31464530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNA Surveillance: The Ends Justify the Means.Chem Rev. 2018 Apr 25;118(8):4422-4447. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00462. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29023106 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrade J. M., Pobre V., Silva I. J., Domingues S., Arraiano C. M. (2009) The role of 3′-5′ exoribonucleases in RNA degradation. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 85, 187–229 - PubMed
-
- Deutscher M. P. (2003) Degradation of stable RNA in bacteria. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 45041–45044 - PubMed
-
- Arraiano C. M., Andrade J. M., Domingues S., Guinote I. B., Malecki M., Matos R. G., Moreira R. N., Pobre V., Reis F. P., Saramago M., Silva I. J., Viegas S. C. (2010) The critical role of RNA processing and degradation in the control of gene expression. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 34, 883–923 - PubMed
-
- Mackie G. A., (2013) RNase E. At the interface of bacterial RNA processing and decay. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11, 45–57 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

