Acquired esophagobronchial fistula without Ono's sign and with unusual cause
- PMID: 24022907
- PMCID: PMC3794269
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-201138
Acquired esophagobronchial fistula without Ono's sign and with unusual cause
Abstract
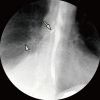
A 60-year-old woman presented with dyspnoea and respirophasic chest discomfort, as well as a history of idiopathic oesophageal diverticulum. Physical examinations showed no evidence of Ono's sign, fever and weight loss. Chest radiograph revealed a right-sided transudative pleural effusion. Barium oesophagogram made a diagnosis of acquired esophagobronchial fistula communicating between oesophagus and bronchus. The oesophagobronchial fistula, causing pleural effusions, was very small and could be caused by idiopathic oesophageal diverticulum. The pleural effusion was removed by thoracentesis, which improved her symptoms. Surgical therapy or covered oesophageal stenting was advised, but she declined. She is followed-up regularly on an outpatient basis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bronchoesophageal fistula secondary to esophageal diverticulum in an adult: a case report and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2021 Feb;49(2):300060521992234. doi: 10.1177/0300060521992234. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33596687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophagobronchial fistula secondary to ruptured traction diverticulum.Gastrointest Radiol. 1977 Oct 25;2(2):119-21. doi: 10.1007/BF02256481. Gastrointest Radiol. 1977. PMID: 98387
-
Esophagobronchial fistula caused by traction esophageal diverticulum.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003 Jan;23(1):128-30. doi: 10.1016/s1010-7940(02)00666-8. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003. PMID: 12493524
-
[Epiphrenic oesophageal diverticulum with an oesophagobronchial fistula resulting in a lung abscess].Ugeskr Laeger. 2016 Nov 21;178(47):V07160523. Ugeskr Laeger. 2016. PMID: 27908313 Danish.
-
[Congenital esophagobronchial fistula communicated to esophageal diverticulum, report of a case].Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1990 Feb;38(2):318-23. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 1990. PMID: 2112181 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Bronchoesophageal fistula secondary to esophageal diverticulum in an adult: a case report and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2021 Feb;49(2):300060521992234. doi: 10.1177/0300060521992234. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33596687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Light RW. The undiagnosed pleural effusion. Clin Chest Med 2006;2013:309–19 - PubMed
-
- Fysh ETH, Shrestha RL, Wood BA, et al. A pleural effusion of multiple causes. Chest 2012;2013:1094–7 - PubMed
-
- Pickhardt PJ, Bhalla S, Balfe DM. Acquired gastrointestinal fistulas: classification, etiologies, and imaging evaluation. Radiology 2002;2013:9–23 - PubMed
-
- Kaul DR, Orringer MB, Saint S, et al. Clinical problem-solving. The Drenched Doctor—a 55-year-old male physician was seen in August because of a 1-week history of fever and night sweats. N Engl J Med 2007;2013:1871–6 - PubMed
-
- Moersch HJ, Schmidt HW. Esophagobronchial fistula. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 1937;2013:689–92
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
