M1 muscarinic receptor activation mediates cell death in M1-HEK293 cells
- PMID: 24023725
- PMCID: PMC3759376
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072011
M1 muscarinic receptor activation mediates cell death in M1-HEK293 cells
Abstract
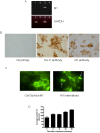
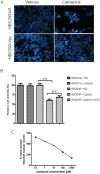
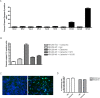
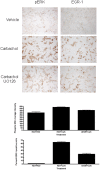
HEK293 cells have been used extensively to generate stable cell lines to study G protein-coupled receptors, such as muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). The activation of M1 mAChRs in various cell types in vitro has been shown to be protective. To further investigate M1 mAChR-mediated cell survival, we generated stable HEK293 cell-lines expressing the human M1 mAChR. M1 mAChRs were efficiently expressed at the cell surface and efficiently internalised within 1 h by carbachol. Carbachol also induced early signalling cascades similar to previous reports. Thus, ectopically expressed M1 receptors behaved in a similar fashion to the native receptor over short time periods of analysis. However, substantial cell death was observed in HEK293-M1 cells within 24 h after carbachol application. Death was only observed in HEK cells expressing M1 receptors and fully blocked by M1 antagonists. M1 mAChR-stimulation mediated prolonged activation of the MEK-ERK pathway and resulted in prolonged induction of the transcription factor EGR-1 (>24 h). Blockade of ERK signalling with U0126 did not reduce M1 mAChR-mediated cell-death significantly but inhibited the acute induction of EGR-1. We investigated the time-course of cell death using time-lapse microscopy and xCELLigence technology. Both revealed the M1 mAChR cytotoxicity occurs within several hours of M1 activation. The xCELLigence assay also confirmed that the ERK pathway was not involved in cell-death. Interestingly, the MEK blocker did reduce carbachol-mediated cleaved caspase 3 expression in HEK293-M1 cells. The HEK293 cell line is a widely used pharmacological tool for studying G-protein coupled receptors, including mAChRs. Our results highlight the importance of investigating the longer term fate of these cells in short term signalling studies. Identifying how and why activation of the M1 mAChR signals apoptosis in these cells may lead to a better understanding of how mAChRs regulate cell-fate decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Wess J (2004) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice: novel phenotypes and clinical implications. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44: 423–450. - PubMed
-
- Dragunow M (2008) M3 muscarinic receptors as targets for drug development in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7: 1 p following p185. - PubMed
-
- Yan GM, Lin SZ, Irwin RP, Paul SM (1995) Activation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors blocks apoptosis of cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Mol Pharmacol 47: 248–257. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

