A novel insight on signal transduction mechanism of RcsCDB system in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
- PMID: 24023746
- PMCID: PMC3762810
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072527
A novel insight on signal transduction mechanism of RcsCDB system in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium
Abstract
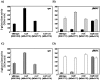
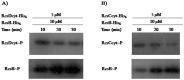
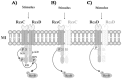
The RcsCDB system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is implicated in the control of capsule and flagella synthesis. The hybrid sensor RcsC, the phosphotransferase RcsD and the RcsB regulator, constitute the main components of the RcsCDB system. The proposed Rcs signaling cascade involves the autophosphorylation of RcsC and the transfer of the phosphate group to RcsB, mediated by RcsD. We previously reported that the overexpression of rcsB repress the transcription of rcsD by an autoregulation mechanism. Moreover, we demonstrated that during the rcsD repression, the RcsB-dependent flagellar modulation remained active. These results suggest that the Rcs phosphorelay mechanism occurs even in the absence of RcsD. In this work, we established the existence of two alternative phosphorelay pathways driving activation of this system. We demonstrated that RcsC and RcsD can act as histidine kinase proteins which, after autophosphorylated, are able to independently transfer the phosphate to RcsB. Our results suggest that these pathways could be activated by different environmental signals, leading different levels of RcsB-phosphorylated to produce a differential gene modulation. These findings contribute to a better understanding of the complexity and importance of the Rcs system activation, where more than one phosphate flow pathway increases the possibilities to exert gene regulation for a quick environmental changes response.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


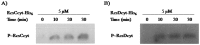
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional autoregulation of the RcsCDB phosphorelay system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microbiology (Reading). 2010 Dec;156(Pt 12):3513-3521. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.041319-0. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Microbiology (Reading). 2010. PMID: 20724387
-
Identification of a new promoter for the response regulator rcsB expression in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009 Nov;300(2):165-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2009.01771.x. Epub 2009 Aug 28. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19780840
-
Salmonella biofilm development depends on the phosphorylation status of RcsB.J Bacteriol. 2012 Jul;194(14):3708-22. doi: 10.1128/JB.00361-12. Epub 2012 May 11. J Bacteriol. 2012. PMID: 22582278 Free PMC article.
-
The Rcs phosphorelay: more than just a two-component pathway.Future Microbiol. 2010 Aug;5(8):1173-84. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.83. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20722597 Review.
-
The Rcs phosphorelay: a complex signal transduction system.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:379-405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.59.050405.101230. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16153174 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulatory Effect of SlyA on rcsB Expression in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2019 Jan 28;201(4):e00673-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00673-18. Print 2019 Feb 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30510144 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Whole-Genome Sequencing and Multimodel Phenotyping To Identify Genetic Predictors of Salmonella Virulence.mSphere. 2020 Jun 10;5(3):e00293-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00293-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32522778 Free PMC article.
-
IgaA negatively regulates the Rcs Phosphorelay via contact with the RcsD Phosphotransfer Protein.PLoS Genet. 2020 Jul 27;16(7):e1008610. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008610. eCollection 2020 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32716926 Free PMC article.
-
The phosphorelay BarA/SirA activates the non-cognate regulator RcsB in Salmonella enterica.PLoS Genet. 2020 May 11;16(5):e1008722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008722. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Genet. 2020. PMID: 32392214 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback Control of Two-Component Regulatory Systems.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep 8;70:103-24. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095331. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27607549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Majdalani N, Gottesman S (2005) The Rcs Phosphorelay: A Complex Signal Transduction System. Annu Rev Microbiol 59: 379–405. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Calderon CB, Garcia-Quintanilla M, Casadesus J, Ramos-Morales F (2005) Virulence attenuation in Salmonella enterica rcsC mutants with constitutive activation of the Rcs system. Microbiology 151: 579–588. - PubMed
-
- Takeda S, Fujisawa Y, Matsubara M, Aiba H, Mizuno T (2001) A novel feature of the multistep phosphorelay in Escherichia coli: a revised model of the RcsC –> YojN –> RcsB signalling pathway implicated in capsular synthesis and swarming behaviour. Mol Microbiol 40: 440–450. - PubMed
-
- Bader MW, Navarre WW, Shiau W, Nikaido H, Frye JG, et al. (2003) Regulation of Salmonella typhimurium virulence gene expression by cationic antimicrobial peptides. Mol Microbiol 50: 219–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

