Variation in thermal performance of a widespread pathogen, the amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
- PMID: 24023908
- PMCID: PMC3762749
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073830
Variation in thermal performance of a widespread pathogen, the amphibian chytrid fungus Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
Abstract
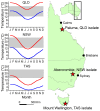
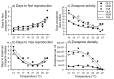
Rates of growth and reproduction of the pathogens that cause emerging infectious diseases can be affected by local environmental conditions; these conditions can thus influence the strength and nature of disease outbreaks. An understanding of these relationships is important for understanding disease ecology and developing mitigation strategies. Widespread emergence of the fungal disease chytridiomycosis has had devastating effects on amphibian populations. The causative pathogen, Batrachochytriumdendrobatidis (Bd), is sensitive to temperature, but its thermal tolerances are not well studied. We examined the thermal responses of three Bd isolates collected across a latitudinal gradient in eastern Australia. Temperature affected all aspects of Bd growth and reproduction that we measured, in ways that often differed among Bd isolates. Aspects of growth, reproduction, and their relationships to temperature that differed among isolates included upper thermal maxima for growth (26, 27, or 28 °C, depending on the isolate), relationships between zoospore production and temperature, and zoospore activity and temperature. Two isolates decreased zoospore production as temperature increased, whereas the third isolate was less fecund overall, but did not show a strong response to temperature until reaching the upper limit of its thermal tolerance. Our results show differentiation in life-history traits among isolates within Australia, suggesting that the pathogen may exhibit local adaptation. An understanding of how environmental temperatures can limit pathogens by constraining fitness will enhance our ability to assess pathogen dynamics in the field, model pathogen spread, and conduct realistic experiments on host susceptibility and disease transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- Harvell CD, Mitchell CE, Ward JR, Altizer S, Dobson AP et al. (2002) Climate warming and disease risks for terrestrial and marine biota. Science 296: 2158-2162. doi:10.1126/science.1063699. PubMed: 12077394. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hawkins CE, Baars C, Hesterman H, Hocking GJ, Jones ME et al. (2006) Emerging disease and population decline of an island endemic, the Tasmanian devil Sarcophilus harrisii . Biol Conserv 131: 307-324. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2006.04.010. - DOI
-
- Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD (2000) Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife – threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 287: 443–449. doi:10.1126/science.287.5452.443. PubMed: 10642539. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daskin JH, Alford RA (2012) Context-dependent symbioses and their potential roles in wildlife diseases. Proc R Soc Lond B 279: 1457-1465. doi:10.1098/rspb.2011.2276. PubMed: 22237907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

