Fibromyalgia: anti-inflammatory and stress responses after acute moderate exercise
- PMID: 24023948
- PMCID: PMC3762808
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074524
Fibromyalgia: anti-inflammatory and stress responses after acute moderate exercise
Abstract
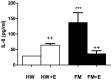
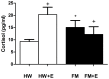
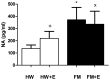
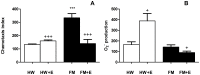
Fibromyalgia (FM) is characterized in part by an elevated inflammatory status, and "modified exercise" is currently proposed as being a good therapeutic help for these patients. However, the mechanisms involved in the exercise-induced benefits are still poorly understood. The objective was to evaluate the effect of a single bout of moderate cycling (45 min at 55% VO2 max) on the inflammatory (serum IL-8; chemotaxis and O2 (-) production by neutrophils; and IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and IL-18 release by monocytes) and stress (cortisol; NA; and eHsp72) responses in women diagnosed with FM compared with an aged-matched control group of healthy women (HW). IL-8, NA, and eHsp72 were determined by ELISA. Cytokines released by monocytes were determined by Bio-Plex® system (LUMINEX). Cortisol was determined by electrochemoluminiscence, chemotaxis was evaluated in Boyden chambers and O2 (-) production by NBT reduction. In the FM patients, the exercise induced a decrease in the systemic concentration of IL-8, cortisol, NA, and eHsp72; as well as in the neutrophil's chemotaxis and O2 (-) production and in the inflammatory cytokine release by monocytes. This was contrary to the completely expected exercise-induced increase in all those biomarkers in HW. In conclusion, single sessions of moderate cycling can improve the inflammatory status in FM patients, reaching values close to the situation of aged-matched HW at their basal status. The neuroendocrine mechanism seems to be an exercise-induced decrease in the stress response of these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

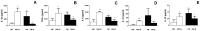
References
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, et al. (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 33: 160–172. - PubMed
-
- Mannerkorpi K, Iversen MD (2003) Physical exercise in fibromyalgia and related syndromes. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 21: 513–534. - PubMed
-
- Van West D, Maes M (2001) Neuroendocrine and immune aspects of fibromyalgia. Biodrugs 15: 521–531. - PubMed
-
- Ploeger HE, Takken T, de Greef MH, Timmons BW (2009) The effects of acute and chronic exercise on inlammatory markers in children and adults with a chronic inflammatory disease: a systematic review. Exerc Immunol Rev 15: 6–41. - PubMed
-
- Petersen AMW, Pedersen BK (2005) The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J Appl Physiol 98: 1154–1162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

