Stem cell recruitment of newly formed host cells via a successful seduction? Filling the gap between neurogenic niche and injured brain site
- PMID: 24023965
- PMCID: PMC3762783
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074857
Stem cell recruitment of newly formed host cells via a successful seduction? Filling the gap between neurogenic niche and injured brain site
Abstract
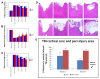
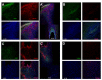
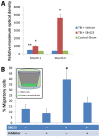
Here, we report that a unique mechanism of action exerted by stem cells in the repair of the traumatically injured brain involves their ability to harness a biobridge between neurogenic niche and injured brain site. This biobridge, visualized immunohistochemically and laser captured, corresponded to an area between the neurogenic subventricular zone and the injured cortex. That the biobridge expressed high levels of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases characterized initially by a stream of transplanted stem cells, but subsequently contained only few to non-detectable grafts and overgrown by newly formed host cells, implicates a novel property of stem cells. The transplanted stem cells manifest themselves as pathways for trafficking the migration of host neurogenic cells, but once this biobridge is formed between the neurogenic site and the injured brain site, the grafted cells disappear and relinquish their task to the host neurogenic cells. Our findings reveal that long-distance migration of host cells from the neurogenic niche to the injured brain site can be achieved through transplanted stem cells serving as biobridges for initiation of endogenous repair mechanisms. This is the first report of a stem cell-paved "biobridge". Indeed, to date the two major schools of discipline in stem cell repair mechanism primarily support the concept of "cell replacement" and bystander effects of "trophic factor secretion". The present novel observations of a stem cell seducing a host cell to engage in brain repair advances basic science concepts on stem cell biology and extracellular matrix, as well as provokes translational research on propagating this stem cell-paved biobridge beyond cell replacement and trophic factor secretion for the treatment of traumatic brain injury and other neurological disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Joyner AL, Skarnes WC, Rossant J (1989) Production of a mutation in mouse En-2 gene by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Nature 338: 153-156. doi:10.1038/338153a0. PubMed: 2563902. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yasuhara T, Matsukawa N, Hara K, Yu G, Xu L et al. (2006) Transplantation of human neural stem cells exerts neuroprotection in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 26: 12497-12511. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3719-06.2006. PubMed: 17135412. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yasuhara T, Hara K, Maki M, Mays RW, Deans RJ et al. (2008) Intravenous grafts recapitulate the neurorestoration afforded by intracerebrally delivered multipotent adult progenitor cells in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28: 1804-1810. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2008.68. PubMed: 18594556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borlongan CV, Hadman M, Sanberg CD, Sanberg PR (2004) Central nervous system entry of peripherally injected umbilical cord blood cells is not required for neuroprotection in stroke. Stroke 35: 2385-2389. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000141680.49960.d7. PubMed: 15345799. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pastori C, Librizzi L, Breschi GL, Regondi C, Frassoni C et al. (2008) Arterially perfused neurosphere-derived cells distribute outside the ischemic core in a model of transient focal ischemia and reperfusion in vitro. PLOS ONE 3: e2754. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002754. PubMed: 18648648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

