The breadth of FGF21's metabolic actions are governed by FGFR1 in adipose tissue
- PMID: 24024127
- PMCID: PMC3757657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2012.08.007
The breadth of FGF21's metabolic actions are governed by FGFR1 in adipose tissue
Abstract
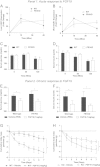
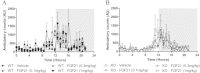
FGF21 is a multifunctional metabolic regulator. The co-factor βKlotho (KLB) allows FGF21 to signal via FGF receptors. Given the widespread nature of FGFR expression and KLB presence in several organs, it remains unclear which tissue/FGFR isoform determine FGF21 action. Here we show that deletion of FGFR1 in fat (FR1KO) leads to a complete ablation of FGF21 stimulated transcriptional activity in this tissue. Furthermore, FR1KO mice showed no FGF21-mediated lowering of plasma glucose, insulin and triglycerides, altered serum levels of adipokines, no increase in energy expenditure, but preserved reductions in serum/liver FFAs as compared to wild type mice. Of importance, the anti-glycaemic actions of FGF19 were fully evident in FR1KO mice implying that FGF19 functions in a FGFR1/adipose independent manner. Taken together, our findings reveal the existence of an adipose FGFR1 driven axis of cross-tissue communication which defines several aspects of FGF21 biology and delineates mechanistic distinctions between FGF21 and FGF19.
Keywords: ACADL, Long chain acetyl-CoA dehydrogenase; ACADVL, Very long chain acetyl-CoA dehydrogenase.; Adipose tissue; BAT, Brown adipose tissue; DIO, Diet induced obese; EGR1, Early growth response protein 1; FFA, Free fatty acids; FGF19; FGF19, Fibroblast growth factor 19; FGF21; FGF21, Fibroblast growth factor 21; FGFR, Fibroblast growth factor receptor; FGFR1; KLB, βKlotho; PGC1α, PPARγ coactivator 1α; SCD1, Stearoyl-Coenzyme A desaturase 1; TG, Triglycerides; UCP1, Uncoupling protein 1; WAT, White adipose tissue; βHB, β-HydroxyButyrate.
Figures



References
-
- Kharitonenkov A., Dunbar J.D., Bina H.A., Bright S., Moyers J.S. FGF-21/FGF-21 receptor interaction and activation is determined by betaKlotho. Journal of Cellular Physiology. 2008;215:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Kharitonenkov A., Larsen P. FGF21 reloaded: challenges of a rapidly growing field. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2011;22:81–86. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
