Lipofuscin: formation, effects and role of macroautophagy
- PMID: 24024146
- PMCID: PMC3757681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.01.006
Lipofuscin: formation, effects and role of macroautophagy
Abstract
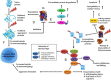
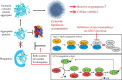
Oxidative stress plays a crucial role in the development of the aging process and age dependent diseases. Both are closely connected to disturbances of proteostasis by protein oxidation and an impairment of the proteasomal system. The final consequence is the accumulation of highly cross-linked undegradable aggregates such as lipofuscin. These aggregates of damaged proteins are detrimental to normal cell functions. Here we provide an overview about effect of these aggregates on the proteasomal system, followed by transcription factor activation and loss of cell viability. Furthermore, findings on the mechanism of radical genesis, proteasomal inhibition and the required components of lipofuscin formation were resumed.
Keywords: Aging; Autophagy; Lipofuscin; Oxidative stress; Proteasome.
Figures


References
-
- Grune T., Reinheckel T., Davies K.J. Degradation of oxidized proteins in K562 human hematopoietic cells by proteasome. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:15504–15509. - PubMed
-
- Pacifici R.E., Kono Y., Davies K.J. Hydrophobicity as the signal for selective degradation of hydroxyl radical-modified hemoglobin by the multicatalytic proteinase complex, proteasome. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1993;268:15405–15411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

