Degenerative spondylolisthesis is associated with low spinal bone density: a comparative study between spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis
- PMID: 24024179
- PMCID: PMC3760191
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/123847
Degenerative spondylolisthesis is associated with low spinal bone density: a comparative study between spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis
Abstract
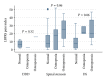
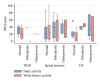
Spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis share many symptoms and the same treatment, but their causes remain unclear. Bone mineral density has been suggested to play a role. The aim of this study was to investigate differences in spinal bone density between spinal stenosis and degenerative spondylolisthesis patients. 81 patients older than 60 years, who underwent DXA-scanning of their lumbar spine one year after a lumbar spinal fusion procedure, were included. Radiographs were assessed for disc height, vertebral wedging, and osteophytosis. Pain was assessed using the Low Back Pain Rating Scale pain index. T-score of the lumbar spine was significantly lower among degenerative spondylolisthesis patients compared with spinal stenosis patients (-1.52 versus -0.52, P = 0.04). Thirty-nine percent of degenerative spondylolisthesis patients were classified as osteoporotic and further 30% osteopenic compared to only 9% of spinal stenosis patients being osteoporotic and 30% osteopenic (P = 0.01). Pain levels tended to increase with poorer bone status (P = 0.06). Patients treated surgically for symptomatic degenerative spondylolisthesis have much lower bone mass than patients of similar age treated surgically for spinal stenosis. Low BMD might play a role in the development of the degenerative spondylolisthesis, further studies are needed to clarify this.
Figures

References
-
- Deyo RA, Gray DT, Kreuter W, Mirza S, Martin BI. United States trends in lumbar fusion surgery for degenerative conditions. Spine. 2005;30(12):1441–1445. - PubMed
-
- Battié MC, Videman T. Lumbar disc degeneration: epidemiology and genetics. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery A. 2006;88(supplement 2):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Love TW, Fagan AB, Fraser RD. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. Developmental or acquired? Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery B. 1999;81(4):670–674. - PubMed
-
- Toyone T, Ozawa T, Kamikawa K, et al. Facet joint orientation difference between cephalad and caudad portions: a possible cause of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2009;34(21):2259–2262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

