The authors reply
- PMID: 24024240
- PMCID: PMC7297210
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwt118
The authors reply
Figures
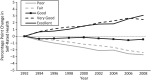

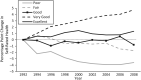

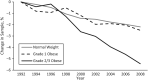
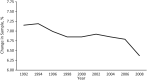
Comment on
-
Obesity and US mortality risk over the adult life course.Am J Epidemiol. 2013 Mar 1;177(5):431-42. doi: 10.1093/aje/kws325. Epub 2013 Feb 3. Am J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23380043 Free PMC article.
-
Re: "obesity and US mortality risk over the adult life course".Am J Epidemiol. 2013 Jul 15;178(2):320. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwt117. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Am J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23792893 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

