miR-204 mediated loss of Myeloid cell leukemia-1 results in pancreatic cancer cell death
- PMID: 24025188
- PMCID: PMC3848798
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-105
miR-204 mediated loss of Myeloid cell leukemia-1 results in pancreatic cancer cell death
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal human malignancies, with an all-stage 5-year survival of <5%, mainly due to lack of effective available therapies. Cancer cell survival is dependent upon up-regulation of the pro-survival response, mediated by anti-apoptotic proteins such as Mcl-1.
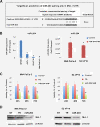
Results: Here we show that over-expression of Mcl-1 in pancreatic patient tumor samples is linked to advancement of the disease. We have previously shown that triptolide, a diterpene triepoxide, is effective both in vitro and in vivo, in killing pancreatic cancer cells. Decrease of Mcl-1 levels, either by siRNA or by treatment with triptolide results in cell death. Using pancreatic cancer cell lines, we have shown that miR-204, a putative regulator of Mcl-1, is repressed in cancer cell lines compared to normal cells. Over-expression of miR-204, either by a miR-204 mimic, or by triptolide treatment results in a decrease in Mcl-1 levels, and a subsequent decrease in cell viability. Using luciferase reporter assays, we confirmed the ability of miR-204 to down-regulate Mcl-1 by directly binding to the Mcl-1 3' UTR. Using human xenograft samples treated with Minnelide, a water soluble variant of triptolide, we have shown that miR-204 is up-regulated and Mcl-1 is down-regulated in treated vs. control tumors.
Conclusion: Triptolide mediated miR-204 increase causes pancreatic cancer cell death via loss of Mcl-1.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

