4-thiouridine inhibits rRNA synthesis and causes a nucleolar stress response
- PMID: 24025460
- PMCID: PMC3866244
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.26214
4-thiouridine inhibits rRNA synthesis and causes a nucleolar stress response
Abstract
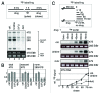
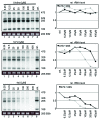
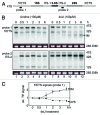
High concentrations (> 100 µM) of the ribonucleoside analog 4-thiouridine (4sU) is widely used in methods for RNA analysis like photoactivatable-ribonucleoside-enhanced crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP) and nascent messenger (m)RNA labeling (4sU-tagging). Here, we show that 4sU-tagging at low concentrations ≤ 10 µM can be used to measure production and processing of ribosomal (r)RNA. However, elevated concentrations of 4sU (> 50 µM), which are usually used for mRNA labeling experiments, inhibit production and processing of 47S rRNA. The inhibition of rRNA synthesis is accompanied by nucleoplasmic translocation of nucleolar nucleophosmin (NPM1), induction of the tumor suppressor p53, and inhibition of proliferation. We conclude that metabolic labeling of RNA by 4sU triggers a nucleolar stress response, which might influence the interpretation of results. Therefore, functional ribosome biogenesis, nucleolar integrity, and cell cycle should be addressed in 4sU labeling experiments.
Keywords: 4-thiouridine; RNA labeling; nucleolar stress; nucleophosmin; p53; rRNA processing; ribosomal RNA.
Figures


References
-
- Pestov DG, Lapik YR, Lau LF. Assays for ribosomal RNA processing and ribosome assembly. Current protocols in cell biology / editorial board, Juan S Bonifacino [et al] 2008; Chapter 22:Unit 22 11 - PubMed
-
- Hafner M, Landthaler M, Burger L, Khorshid M, Hausser J, Berninger P, Rothballer A, Ascano M, Jr., Jungkamp AC, Munschauer M, et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of RNA-binding protein and microRNA target sites by PAR-CLIP. Cell. 2010;141:129–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
