The reuniens and rhomboid nuclei: neuroanatomy, electrophysiological characteristics and behavioral implications
- PMID: 24025745
- PMCID: PMC4975011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.08.006
The reuniens and rhomboid nuclei: neuroanatomy, electrophysiological characteristics and behavioral implications
Abstract
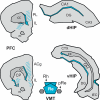
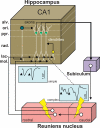
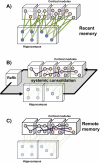
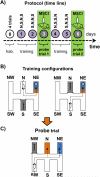
The reuniens and rhomboid nuclei, located in the ventral midline of the thalamus, have long been regarded as having non-specific effects on the cortex, while other evidence suggests that they influence behavior related to the photoperiod, hunger, stress or anxiety. We summarise the recent anatomical, electrophysiological and behavioral evidence that these nuclei also influence cognitive processes. The first part of this review describes the reciprocal connections of the reuniens and rhomboid nuclei with the medial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus. The connectivity pattern among these structures is consistent with the idea that these ventral midline nuclei represent a nodal hub to influence prefrontal-hippocampal interactions. The second part describes the effects of a stimulation or blockade of the ventral midline thalamus on cortical and hippocampal electrophysiological activity. The final part summarizes recent literature supporting the emerging view that the reuniens and rhomboid nuclei may contribute to learning, memory consolidation and behavioral flexibility, in addition to general behavior and aspects of metabolism.
Keywords: 5-CSRT; 5-choice serial reaction time; Alv; Behavioral flexibility; CRF; DNMTP; EEG; FG; FR; GABA; Hippocampus; IL; LTP; Lac-mol; MFB; MdT; Medial prefrontal cortex; N-methyl-D-aspartate; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NGF; NMDA; NMDAR; Nerve growth factor; Non specific thalamus; Ori; PHA-L; PL; Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin; Re; Reference memory; Reuniens nucleus; Rh; Rhomboid nucleus; Spatial memory; Systems-level consolidation; Ventral midline thalamus; Working memory; alveus; corticotrophin releasing factor; delayed nonmatching to place (or to position); electroencephalogram or electroencephalographic; fluorogold; fluororuby; gamma aminobutyric acid; infralimbic cortex; long term potentiation; mPFC; medial forebrain bundle; medial prefrontal cortex; midline thalamus; mol; pRe; perireuniens nucleus; prelimbic cortex; pyr; rad; reuniens nucleus; rhomboid nucleus; sEPSCs; spontaneous excitatory post-synaptic currents; stratum lacunosum-moleculare; stratum moleculare; stratum oriens; stratum pyramidale; stratum radiatum.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Abela AR, Dougherty SD, Fagen ED, Hill CJ, Chudasama Y. Inhibitory control deficits in rats with ventral hippocampal lesions. Cereb. Cortex. 2013;23(6):1396–1409. - PubMed
-
- Aggleton JP, Brown MW. Episodic memory, amnesia, and the hippocampal-anterior thalamic axis. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999;22:425–444. - PubMed
-
- Amici S. Thalamic infarcts and haemorrhages. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2012;30:132–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

