Chaperone machines for protein folding, unfolding and disaggregation
- PMID: 24026055
- PMCID: PMC4340576
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3658
Chaperone machines for protein folding, unfolding and disaggregation
Abstract
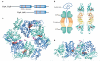
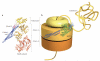
Molecular chaperones are diverse families of multidomain proteins that have evolved to assist nascent proteins to reach their native fold, protect subunits from heat shock during the assembly of complexes, prevent protein aggregation or mediate targeted unfolding and disassembly. Their increased expression in response to stress is a key factor in the health of the cell and longevity of an organism. Unlike enzymes with their precise and finely tuned active sites, chaperones are heavy-duty molecular machines that operate on a wide range of substrates. The structural basis of their mechanism of action is being unravelled (in particular for the heat shock proteins HSP60, HSP70, HSP90 and HSP100) and typically involves massive displacements of 20-30 kDa domains over distances of 20-50 Å and rotations of up to 100°.
Figures



References
-
- Korennykh A, Walter P. Structural basis of the unfolded protein response. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012;28:251–277. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Bracher A, Hayer-Hartl M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature. 2011;475:324–332. - PubMed
-
- Bukau B, Weissman J, Horwich A. Molecular chaperones and protein quality control. Cell. 2006;125:443–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

