Central losartan attenuates increases in arterial pressure and expression of FosB/ΔFosB along the autonomic axis associated with chronic intermittent hypoxia
- PMID: 24026072
- PMCID: PMC3840317
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00541.2012
Central losartan attenuates increases in arterial pressure and expression of FosB/ΔFosB along the autonomic axis associated with chronic intermittent hypoxia
Abstract
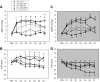
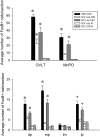
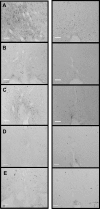
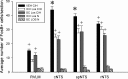
Chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH) increases mean arterial pressure (MAP) and FosB/ΔFosB staining in central autonomic nuclei. To test the role of the brain renin-angiotensin system (RAS) in CIH hypertension, rats were implanted with intracerebroventricular (icv) cannulae delivering losartan (1 μg/h) or vehicle (VEH) via miniosmotic pumps and telemetry devices for arterial pressure recording. A third group was given the same dose of losartan subcutaneously (sc). Two groups of losartan-treated rats served as normoxic controls. Rats were exposed to CIH or normoxia for 7 days and then euthanized for immunohistochemistry. Intracerebroventricular losartan attenuated CIH-induced increases in arterial pressure during CIH exposure (0800-1600 during the light phase) on days 1, 6, and 7 and each day during the normoxic dark phase. FosB/ΔFosB staining in the organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), median preoptic nucleus (MnPO), paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN), the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), and the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) was decreased in icv losartan-treated rats. Subcutaneous losartan also reduced CIH hypertension during the last 2 days of CIH and produced bradycardia prior to the effect on blood pressure. Following sc losartan, FosB/ΔFosB staining was reduced only in the OVLT, MnPO, PVN, and NTS. These data indicate that the central and peripheral RAS contribute to CIH-induced hypertension and transcriptional activation of autonomic nuclei and that the contribution of the central RAS is greater during the normoxic dark phase of CIH hypertension.
Keywords: angiotensin; blood pressure; hypertension; sleep apnea.
Figures


References
-
- Allen AM, Zhuo J, Mendelsohn FA. Localization and function of angiotensin AT1 receptors. Am J Hypertens 13: 31S–38S, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Bohlender J, Imboden H. Angiotensinergic neurotransmission in the peripheral autonomic nervous system. Front Biosci 17: 2419–2432, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Brody MJ, Fink GD, Buggy J, Haywood JR, Gordon FJ, Johnson AK. The role of the anteroventral third ventricle (AV3V) region in experimental hypertension. Circ Res 43: I2–I13, 1978 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

