Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a risk marker of the attenuated relationship between serum cholesterol and cardiovascular events at older age. The ARIC Study
- PMID: 24026395
- PMCID: PMC3783092
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwt086
Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a risk marker of the attenuated relationship between serum cholesterol and cardiovascular events at older age. The ARIC Study
Abstract
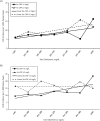
The relationship between cholesterol and coronary heart disease (CHD) is attenuated at older age. We analyzed cholesterol level as a predictor of CHD in 8,947 participants from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study, a large multicenter cohort study that enrolled participants in 1987-1989 at 4 field centers in Washington County, Maryland; Forsyth County, North Carolina; Jackson, Mississippi; and Minneapolis, Minnesota. Participants in the present analysis had no history of CHD and were stratified by age (<65 or ≥65 years) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level (<2 or ≥2 mg/L). Visit 4 (1996-1997) was the baseline for this analysis, with follow-up through 2008. Cholesterol level was significantly associated with CHD among younger participants, and cholesterol level was similarly predictive of CHD among older participants with an hs-CRP level of <2 mg/L. In contrast, among older participants with an hs-CRP level of 2 mg/L or higher, the association of CHD with total cholesterol level was borderline significant (hazard ratio = 1.14, 95% confidence interval: 1.00, 1.29), and the association of CHD with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level was nonsignificant (hazard ratio = 1.10; 95% confidence interval: 0.96, 1.26). Among older persons with an elevated hs-CRP level, cholesterol level was significantly less predictive of CHD (P < 0.05), whereas for those with an hs-CRP level of <2 mg/L, there was no significant difference compared with younger participants. In conclusion, we found that among the young-old, the association of cholesterol level with CHD was strong when hs-CRP level was not elevated and weak when hs-CRP level was elevated. Therefore, hs-CRP level could be useful for stratifying the young-old to assess the strength of cholesterol level in CHD risk prediction.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; elderly persons; serum cholesterol.
Figures
Comment in
-
Attention to detail in the selection of words in epidemiologic research reports.Am J Epidemiol. 2014 Apr 1;179(7):795-6. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwu008. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Am J Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 24557814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stamler J, Wentworth D, Neaton JD. Is relationship between serum cholesterol and risk of premature death from coronary heart disease continuous and graded? Findings in 356,222 primary screenees of the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT) JAMA. 1986;256(20):2823–2828. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I, et al. Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia. West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333(20):1301–1307. - PubMed
-
- Collins R, Armitage J, Parish S, et al. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361(9374):2005–2016. - PubMed
-
- Kronmal RA, Cain KC, Ye Z, et al. Total serum cholesterol levels and mortality risk as a function of age. A report based on the Framingham data. Arch Intern Med. 1993;153(9):1065–1073. - PubMed
-
- Zimetbaum P, Frishman WH, Ooi WL, et al. Plasma lipids and lipoproteins and the incidence of cardiovascular disease in the very elderly. The Bronx Aging Study. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992;12(4):416–423. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HC055016/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055019/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55016/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055015/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55021/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055020/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55019/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55015/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55020/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055022/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55018/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-55022/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

