A third mitochondrial RNA polymerase in the moss Physcomitrella patens
- PMID: 24026503
- PMCID: PMC3895441
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-013-0405-y
A third mitochondrial RNA polymerase in the moss Physcomitrella patens
Abstract
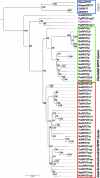
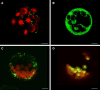
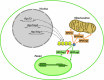
In most organisms, the mitochondrial genes are transcribed by RNA polymerases related to the single-subunit RNA polymerases of bacteriophages like T3 and T7. In flowering plants, duplication(s) of the RpoTm gene coding for the mitochondrial RNA polymerase (RPOTm) led to the evolution of additional RNA polymerases transcribing genes in plastids (RPOTp) or in both mitochondria and plastids (RPOTmp). Two putative RPOTmp enzymes were previously described to be encoded by the nuclear genes RpoTmp1 and RpoTmp2 in the moss Physcomitrella patens. Here, we report on a third Physcomitrella RpoT gene. We determined the sequence of the cDNA. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequence with sequences of plant organellar RNA polymerases suggests that this gene encodes a functional phage-type RNA polymerase. The 78 N-terminal amino acids of the putative RNA polymerase were fused to GFP and found to target the fusion protein exclusively to mitochondria in Arabidopsis protoplasts. P. patens is the only known organism to possess three mitochondrial RNA polymerases.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evolution of plant phage-type RNA polymerases: the genome of the basal angiosperm Nuphar advena encodes two mitochondrial and one plastid phage-type RNA polymerases.BMC Evol Biol. 2010 Dec 6;10:379. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-379. BMC Evol Biol. 2010. PMID: 21134269 Free PMC article.
-
Two RpoT genes of Physcomitrella patens encode phage-type RNA polymerases with dual targeting to mitochondria and plastids.Gene. 2002 May 15;290(1-2):95-105. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00583-8. Gene. 2002. PMID: 12062804
-
Identification and characterization of two phage-type RNA polymerase cDNAs in the moss Physcomitrella patens: implication of recent evolution of nuclear-encoded RNA polymerase of plastids in plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2002 Mar;43(3):245-55. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcf041. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11917078
-
Organellar RNA polymerases of higher plants.Int Rev Cytol. 1999;190:1-59. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62145-2. Int Rev Cytol. 1999. PMID: 10331238 Review.
-
Architecture of the PPR gene family in the moss Physcomitrella patens.RNA Biol. 2013;10(9):1439-45. doi: 10.4161/rna.24772. Epub 2013 Apr 23. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23645116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the study of chloroplast gene expression and its evolution.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Feb 25;5:61. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00061. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24611069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Drummond A, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A, Heled J, Kearse M, Moir R, Stones-Havas S, Sturrock S, Thierer T, Wilson A (2010) Geneious v5.1, available from http://www.geneious.com/ - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

