Cost-effectiveness of MODY genetic testing: translating genomic advances into practical health applications
- PMID: 24026547
- PMCID: PMC3867988
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0410
Cost-effectiveness of MODY genetic testing: translating genomic advances into practical health applications
Abstract
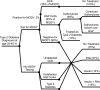
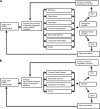
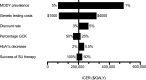
OBJECTIVE To evaluate the cost-effectiveness of a genetic testing policy for HNF1A-, HNF4A-, and GCK-MODY in a hypothetical cohort of type 2 diabetic patients 25-40 years old with a MODY prevalence of 2%. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS We used a simulation model of type 2 diabetes complications based on UK Prospective Diabetes Study data, modified to account for the natural history of disease by genetic subtype to compare a policy of genetic testing at diabetes diagnosis versus a policy of no testing. Under the screening policy, successful sulfonylurea treatment of HNF1A-MODY and HNF4A-MODY was modeled to produce a glycosylated hemoglobin reduction of -1.5% compared with usual care. GCK-MODY received no therapy. Main outcome measures were costs and quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) based on lifetime risk of complications and treatments, expressed as the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) (USD/QALY). RESULTS The testing policy yielded an average gain of 0.012 QALYs and resulted in an ICER of 205,000 USD. Sensitivity analysis showed that if the MODY prevalence was 6%, the ICER would be ~50,000 USD. If MODY prevalence was >30%, the testing policy was cost saving. Reducing genetic testing costs to 700 USD also resulted in an ICER of ~50,000 USD. CONCLUSIONS Our simulated model suggests that a policy of testing for MODY in selected populations is cost-effective for the U.S. based on contemporary ICER thresholds. Higher prevalence of MODY in the tested population or decreased testing costs would enhance cost-effectiveness. Our results make a compelling argument for routine coverage of genetic testing in patients with high clinical suspicion of MODY.
Figures
References
-
- Frayling TM, Evans JC, Bulman MP, et al. beta-cell genes and diabetes: molecular and clinical characterization of mutations in transcription factors. Diabetes 2001;50(Suppl. 1):S94–S100 - PubMed
-
- Tattersall RB, Fajans SS. A difference between the inheritance of classical juvenile-onset and maturity-onset type diabetes of young people. Diabetes 1975;24:44–53 - PubMed
-
- Shields BM, Hicks S, Shepherd MH, Colclough K, Hattersley AT, Ellard S. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY): how many cases are we missing? Diabetologia 2010;53:2504–2508 - PubMed
-
- Shepherd M, Pearson ER, Houghton J, Salt G, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. No deterioration in glycemic control in HNF-1alpha maturity-onset diabetes of the young following transfer from long-term insulin to sulphonylureas. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3191–3192 - PubMed
-
- Pearson ER, Starkey BJ, Powell RJ, Gribble FM, Clark PM, Hattersley AT. Genetic cause of hyperglycaemia and response to treatment in diabetes. Lancet 2003;362:1275–1281 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

