B-lymphocyte depletion with rituximab and β-cell function: two-year results
- PMID: 24026563
- PMCID: PMC3898764
- DOI: 10.2337/dc13-0626
B-lymphocyte depletion with rituximab and β-cell function: two-year results
Abstract
Objective: We previously reported that selective depletion of B-lymphocytes with rituximab, an anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, slowed decline of β-cell function in recent-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) at 1 year. Subjects were followed further to determine whether there was persistence of effect.
Research design and methods: Eighty-seven subjects (aged 8-40 years) were randomly assigned to, and 81 received, infusions of rituximab or placebo on days 1, 8, 15, and 22. The primary outcome-baseline-adjusted mean 2-h area under the curve (AUC) serum C-peptide during a mixed-meal tolerance test (MMTT) at 1 year-showed higher C-peptide AUC with rituximab versus placebo. Subjects were further followed with additional MMTTs every 6 months.
Results: The rate of decline of C-peptide was parallel between groups but shifted by 8.2 months in rituximab-treated subjects. Over 30 months, AUC, insulin dose, and HbA1c were similar for rituximab and placebo. However, in evaluating change in C-peptide over the entire follow-up period, the rituximab group means were significantly larger as compared within assessment times with the placebo group means using a global test (P = 0.03). Odds ratio for loss of C-peptide to <0.2 nmol/L following rituximab was 0.565 (P = 0.064). B-lymphocytes recovered to baseline values by 18 months. Serum IgG levels were maintained in the normal range but IgM levels were depressed.
Conclusions: Like several other immunotherapeutic approaches tested, in recent-onset T1DM, rituximab delays the fall in C-peptide but does not appear to fundamentally alter the underlying pathophysiology of the disease.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00279305.
Figures
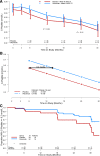
 scale tended to follow a straight line (i.e., two random effects: the intercept and constant decay rate over time). C: Time to C-peptide failure by treatment group. C-peptide failure was defined as the first time at which the maximum C-peptide during a 2-h MMTT was <0.2 nmol/L.
scale tended to follow a straight line (i.e., two random effects: the intercept and constant decay rate over time). C: Time to C-peptide failure by treatment group. C-peptide failure was defined as the first time at which the maximum C-peptide during a 2-h MMTT was <0.2 nmol/L.

References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group Effect of intensive therapy on residual beta-cell function in patients with type 1 diabetes in the diabetes control and complications trial. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1998;128:517–523 - PubMed
-
- Steffes MW, Sibley S, Jackson M, Thomas W. Beta-cell function and the development of diabetes-related complications in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes Care 2003;26:832–836 - PubMed
-
- Herold KC, Hagopian W, Auger JA, et al. Anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody in new-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2002;346:1692–1698 - PubMed
-
- Keymeulen B, Vandemeulebroucke E, Ziegler AG, et al. Insulin needs after CD3-antibody therapy in new-onset type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;352:2598–2608 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK-085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061036/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024982/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001085/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000005/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025761/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061040/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR029890/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001105/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR031986/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024131/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP3 DK097681/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-084565/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000093/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025744/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK-061055/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-085463/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061041/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00400/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117009/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002529/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK097835/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200800019C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK-061016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

