Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke
- PMID: 24026639
- PMCID: PMC6474318
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub3
Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke
Update in
-
Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke: network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Apr 23;4(4):CD000197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32324916 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Organised stroke unit care is provided by multidisciplinary teams that exclusively manage stroke patients in a ward dedicated to stroke patients, with a mobile stroke team or within a generic disability service (mixed rehabilitation ward).
Objectives: To assess the effect of stroke unit care compared with alternative forms of care for people following a stroke.
Search methods: We searched the trials registers of the Cochrane Stroke Group (January 2013) and the Cochrane Effective Practice and Organisation of Care (EPOC) Group (January 2013), MEDLINE (2008 to September 2012), EMBASE (2008 to September 2012) and CINAHL (1982 to September 2012). In an effort to identify further published, unpublished and ongoing trials, we searched 17 trial registers (January 2013), performed citation tracking of included studies, checked reference lists of relevant articles and contacted trialists.
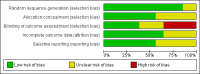
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled clinical trials comparing organised inpatient stroke unit care with an alternative service. After formal risk of bias assessment, we have now excluded previously included quasi-randomised trials.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors initially assessed eligibility and trial quality. We checked descriptive details and trial data with the co-ordinators of the original trials.
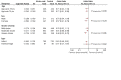
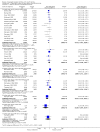
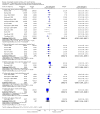
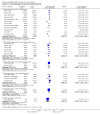
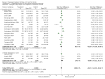
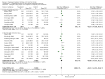
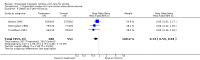
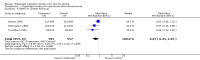
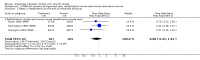
Main results: We included 28 trials, involving 5855 participants, comparing stroke unit care with an alternative service. More-organised care was consistently associated with improved outcomes. Twenty-one trials (3994 participants) compared stroke unit care with care provided in general wards. Stroke unit care showed reductions in the odds of death recorded at final (median one year) follow-up (odds ratio (OR) 0.87, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.69 to 0.94; P = 0.005), the odds of death or institutionalised care (OR 0.78, 95% CI 0.68 to 0.89; P = 0.0003) and the odds of death or dependency (OR 0.79, 95% CI 0.68 to 0.90; P = 0.0007). Sensitivity analyses indicated that the observed benefits remained when the analysis was restricted to securely randomised trials that used unequivocally blinded outcome assessment with a fixed period of follow-up. Outcomes were independent of patient age, sex, initial stroke severity or stroke type, and appeared to be better in stroke units based in a discrete ward. There was no indication that organised stroke unit care resulted in a longer hospital stay.
Authors' conclusions: Stroke patients who receive organised inpatient care in a stroke unit are more likely to be alive, independent, and living at home one year after the stroke. The benefits were most apparent in units based in a discrete ward. We observed no systematic increase in the length of inpatient stay.
Conflict of interest statement
Most of the Stroke Unit Trialists Collaboration members carried out trials that are included in the review.
Figures










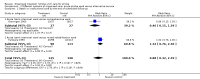
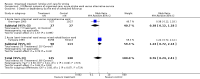





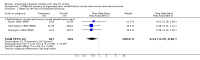
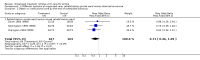


Update of
-
Organised inpatient (stroke unit) care for stroke.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Oct 17;(4):CD000197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 11;(9):CD000197. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000197.pub3. PMID: 17943737 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Athens 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pappa T, Xynos K, Theodorakis M, Salliaris M, Kostopoulos K, Vemmos K. The impact of acute stroke unit treatment on long term survival. Cerebrovascular diseases 2007;23 Suppl 2:64.
-
- Spengos K, Tsivgoulis G, Manios E, Papamichael C, Konstastinopoulou A, Vemmos K. Which patients benefit most from treatment in a stroke unit?. Stroke 2004; Vol. 35, issue 1:294.
-
- Vemmos K, Takis K, Madelos D, Synetos A, Volotasiou V, Tzavellas H. Stroke unit treatment versus general medical wards: long term survival. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2001;11 Suppl 4:8.
Beijing 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ma RH, Wang YJ, Qu H, Yang ZH. Assessment of the early effectiveness of a stroke unit in comparison to the general ward. Chinese Medical Journal 2004;117(6):852‐5. - PubMed
-
- Ma RH, Wang YJ, Zhao XQ, Wang CX, Yang ZH, Qu H. The impact of stroke unit on early outcome of cerebral infarction patients. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2004;43(3):183‐5. - PubMed
Birmingham 1972 {published data only}
-
- Peacock PB, Riley CHP, Lampton TD, Raffel SS, Walker JS. In: Stewart GT editor(s). Trends in Epidemiology: The Birmingham Stroke, Epidemiology and Rehabilitation Study. Springfield, Illinois: Thomas, 1972:231‐345.
Dover 1984 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stevens RS, Ambler NR, Warren MD. A randomised controlled trial of a stroke rehabilitation ward. Age and Ageing 1984;13:65‐75. - PubMed
Dover 1984 (GMW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stevens RS, Ambler NR, Warren MD. A randomised controlled trial of a stroke rehabilitation ward. Age and Ageing 1984; Vol. 13:65‐75. - PubMed
Dover 1984 (MRW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Stevens RS, Ambler NR, Warren MD. A randomised controlled trial of a stroke rehabilitation ward. Age and Ageing 1984; Vol. 13:65‐75. - PubMed
Edinburgh 1980 {published and unpublished data}
Goteborg‐Ostra 1988 {unpublished data only}
-
- Svensson A, Harmsen P, Wilhelmsen L. Goteborg Ostra Stroke Unit Trial. Personal communication.
Goteborg‐Sahlgren 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Claesson L, Gosman‐Hedstrom G, Fagerberg B, Blomstrand C. Hospital re‐admissions in relation to acute stroke unit care versus conventional care in elderly patients the first year after stroke: The Goteborg 70+ stroke study. Age and Ageing 2003;32:109‐13. - PubMed
-
- Claesson L, Gosman‐Hedstrom G, Johannesson M, Fagerberg B, Blomstrand C. Resource utilization and costs of stroke unit care integrated in a care continuum: A 1‐year controlled, prospective, randomized study in elderly patients. The Goteborg 70+ stroke study. Stroke 2000;31:2569‐77. - PubMed
-
- Claesson L, Gosman‐Hedstrom G, Johannesson M, Fagerberg B, Blomstrand C. Stroke unit care ‐ effects on ADL, health‐related quality of life and health economy. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1999;9 Suppl 1:115.
-
- Fagerberg B, Blomstrand C. Do stroke units save lives?. Lancet 1993; Vol. 342:992. - PubMed
-
- Fagerberg B, Claesson L, Gosman‐Hedstrom G, Blomstrand C. Effect of acute stroke unit care integrated with care continuum versus conventional treatment: A randomized 1‐year study of elderly patients. The Goteborg 70+ stroke study. Stroke 2000;31:2578‐84. - PubMed
Groningen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Sulter G, Elting JW, Langedijik M, Maurits NM, Keyser J. Admitting acute ischaemic stroke patients to a stroke care monitoring unit versus a conventional stroke unit; a randomized pilot study. Stroke 2003;34:101‐4. - PubMed
Guangdong 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yang N, LI G, Zhang Z, Wang B. Clinical efficacy observing of the treatment in stroke unit of integrated TCM and western medicine on patients with ischaemic stroke in acute stage. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2008;26:2750‐3.
Guangdong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yang N, Zheng L. Cost benefit and effect analysis for patients with ischaemic stroke on stroke unit of integration traditional Chinese and western medicine. Chinese Archives of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2009;27:1331‐3.
Helsinki 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kaste M, Palomaki H. By whom should elderly stroke patients be treated?. Stroke 1992;23(1):163. - PubMed
-
- Kaste M, Palomaki H. Who should treat elderly stroke patients?. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 1992;2 Suppl 1:S27.
-
- Kaste M, Palomaki H, Sarna S. Where and how should elderly stroke patients be treated? A randomised trial. Stroke 1995;26:249‐53. - PubMed
Huaihua 2004 {published data only}
-
- Liao Y, Zeng JS, Zhou J, Xie CM, Yang DY, Liu SX, et al. Pattern and superiority of stroke unit in treating patients with stroke. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rehabilitation 2004;8:6014‐5.
Hunan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Li X, Wu Q, Liu W. The effects of the treatment in stroke unit of integrated therapy TCM and WM on patients with stroke in acute stage. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine 2007;16(4):381‐3.
Illinois 1966 {published data only}
-
- Gordon EE, Kohn KH. Evaluation of rehabilitation methods in the hemiplegic patient. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1966;19:3‐16. - PubMed
Joinville 2003 {published data only}
-
- Cabral NL, Moro C, Silva GR, Scola RH, Werneck LC. Study comparing the stroke unit outcome and conventional ward treatment: A randomised study in Joinville, Brazil. Arquivos de Neuro‐psiquatria 2003;61(2‐A):188‐93. - PubMed
Kuopio 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sivenius J, Pyorala K, Heinonen OP, Salonen JT, Reikkinen P. The significance of intensity of rehabilitation after stroke ‐ a controlled trial. Stroke 1985;16:928‐31. - PubMed
Manchester 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Dey P, Woodman M, Gibbs A. Fast track assessment and rehabilitation for stroke patients (FASTAR). Report (Project number RD0/28/1/02) 2003.
-
- Dey P, Woodman M, Gibbs A, Steele R, Stocks SJ, Wagstaff S, et al. Early assessment by a mobile stroke team: a randomised controlled trial. Age and Ageing 2005;34:331‐8. - PubMed
Montreal 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wood‐Dauphinee S, Shapiro S, Bass E, Fletcher C, Georges P, Hensby V, et al. A randomised trial of team care following stroke. Stroke 1984;5:864‐72. - PubMed
Newcastle 1993 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Aitken PD, Rodgers H, French JM, Bates D, James OFW. General medical or geriatric unit care for acute stroke? A controlled trial. Age and Ageing 1993;22 Suppl 2:4‐5.
New York 1962 {published data only}
-
- Feldman DJ, Lee PR, Unterecker J, Lloyd K, Rusk HA, Toole A. A comparison of functionally orientated medical care and formal rehabilitation in the management of patients with hemiplegia due to cerebrovascular disease. Journal of Chronic Diseases 1962;15:297‐310. - PubMed
Nottingham 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Drummond A, Lincoln N, Juby L. Effects of stroke unit on knowledge of stroke and experiences in hospital. Age and Ageing 2001;30:129‐33.
-
- Juby LC, Lincoln NB, Berman P. The effect of a stroke rehabilitation unit on functional and psychological outcome. A randomised controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1996;6:106‐10.
Nottingham 1996 (GMW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Juby LC, Lincoln NB, Berman P. The effect of a stroke rehabilitation unit on functional and psychological outcome. A randomised controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1996;6:106‐10.
Nottingham 1996 (MRW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Juby LC, Lincoln NB, Berman P. The effect of a stroke rehabilitation unit on functional and psychological outcome. A randomised controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 1996;6:106‐10.
Orpington 1993 {published and unpublished data}
Orpington 1993 (GMW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kalra L, Dale P, Crome P. Improving stroke rehabilitation: a controlled study. Stroke 1993;24:1462‐7. - PubMed
Orpington 1993 (MRW) {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kalra L, Dale P, Crome P. Improving stroke rehabilitation: a controlled study. Stroke 1993;24:1462‐7. - PubMed
Orpington 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kalra L, Eade J. Role of stroke rehabilitation units in managing severe disability after stroke. Stroke 1995;26:2031‐4. - PubMed
Orpington 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Evans A, Harraf F, Donaldson N, Kalra L. Randomised controlled study of stroke unit care versus stroke team care in different stroke subtypes. Stroke 2002;33:449‐55. - PubMed
-
- Evans A, Perez I, Harraf H, Melbourn A, Steadman J, Donaldson N, et al. Can differences in management processes explain different outcomes between stroke unit and stroke team care?. Lancet 2001;358:1586‐92. - PubMed
-
- Evans A, Perez I, Melbourn A, Steadman J, Kalra L. Alternative strategies in stroke: a randomised controlled trial of three strategies of stroke management and rehabilitation. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2000;10 Suppl 2:60.
-
- Kalra LL, Evans A, Perez I, Knapp M, Donaldson N, Swift C. Alternative strategies for stroke: a prospective randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2000;356:894‐9. - PubMed
-
- Patel A, Knapp M, Perez I, Evans A, Kalra L. Alternative strategies for stroke care: cost‐effectiveness analysis from a prospective randomised controlled trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2003;16 Suppl 4:101.
Perth 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Hankey GJ, Deleo D, Stewart‐Wynne EG. Stroke units: an Australian perspective. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 1997;27:437‐8. - PubMed
Svendborg 1995 {published data only}
-
- Henriksen IO, Laursen SO. Acute stroke ‐ treatment in a non‐intensive stroke unit. Scandinavian Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 1992;Suppl 26:153.
-
- Laursen SO, Henriksen IO, Dons U, Jacobsen B, Gundertofte L. Intensive rehabilitation following stroke: controlled pilot study. Ugeskr Laeger 1995;157:1996‐99. - PubMed
Tampere 1993 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ilmavirta M, Frey H, Erila T, Fogelholm R. Stroke outcome and outcome of brain infarction. A prospective randomised study comparing the outcome of patients with acute brain infarction treated in a stroke unit and in an ordinary neurological ward. Doctoral Thesis. Vol. 410; series A, Tampere: University of Tampere Faculty of Medicine, 1994.
Trondheim 1991 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Indredavik B, Bakke F, Slordahl SA, Rokseth R, Haheim LL. Stroke unit treatment improves long‐term quality of life: a randomized controlled trial. Stroke 1998;29:895‐99. - PubMed
-
- Indredavik B, Bakke F, Slordahl SA, Rokseth R, Haheim LL. Stroke unit treatment: 10 year follow‐up. Stroke 1999;30:1524‐7. - PubMed
-
- Indredavik B, Bakke F, Slordahl SA, Rokseth R, Haheim LL. Treatment in a combined acute and rehabilitation stroke unit. Which aspects are important?. Stroke 1999;30:917‐23. - PubMed
-
- Indredavik B, Bakke F, Solberg R, Rokseth R, Haahein LL, Home I. Benefit of stroke unit: a randomised controlled trial. Stroke 1991;22:1026‐31. - PubMed
-
- Indredavik B, Fjaertoft H, Ekeberg RN, Loge A, Morch B. Benefit of an extended stroke unit service with early supported discharge. A randomised control trial. Stroke 2000;31:2989‐94. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abissi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Abissi CJ, Sepe E, Patiak C, Davis JN. Cerebral infarction: comparison of a care with case‐management to traditional care. Neurology 1995;45 Suppl 4:A240.
Asplund 2000 {published data only}
-
- Asplund K, Gustafson Y, Jacobsson C, Bucht G, Wahlin A, Peterson J, et al. Geriatric‐based general wards for older acute medical patients: a randomized comparison of outcomes and use of resources. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2000;48(11):1381‐8. - PubMed
Cavallini 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Cavallini A, Micieli G, Marcheselli S, Quaglini S. Role of monitoring in the management of acute ischaemic stroke patients. Stroke 2003;34(11):2599‐603. - PubMed
-
- Cavallini A, Micieli G, Zambrelli E, Quaglini S, Rogoni C. Role of continuous physiological monitoring in the acute phase of stroke. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2001;11 Suppl 4:117.
Davis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Davis M, Chambers B, Birschel P. A pilot study of monitoring in acute stroke. Stroke 2000;31(11):2869.
-
- Davis M, Hollymann C, McGiven M, Chambers I, Egbuji J, Barer D. Physiological monitoring in acute stroke. Age and Ageing 1999;28 Suppl 1:45.
Diagana 2008 {published data only}
-
- Diagana M, Ould Abdallahi Salem B, N'Diaye M, LeCornet C, Quet F, et al. Impact of acute unit care improving post‐stroke functionality outcomes in Noukachott, Mauritania. African Journal of Neurological Sciences 2008;27:38‐46.
Di Lauro 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lauro A, Pellegrino L, Savastano G, Ferraro C, Fusco M, Balzarano F, et al. A randomised trial on the efficacy of intensive rehabilitation in the acute phase of ischemic stroke. Journal of Neurology 2003;250(10):1206‐8. - PubMed
Durastanti 2005 {published data only}
-
- Durastanti L, Puca E, Angelantonio E, Lorenzano S, Falcou A, Gori MC, et al. Efficacy of acute ischemic stroke patients management in an emergency department stroke unit (EDSU). Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;19 Suppl 2:57.
HAMLET 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hofmeijer J, Worp HB, Amelink GJ, Algra A, Gijn J, Kapelle LJ. HAMLET hemicraniectomy after MCA infarction with life‐threatening oedema trial (Abstract 11). Proceedings of the European Stroke Conference, 21‐24 May, Valencia, Spain. 2003.
Hamrin 1982 {published and unpublished data}
Koton 2005 {published data only}
-
- Koton S, Schwammenthal Y, Merzeliak O, Philips T, Tsabari R, Bruk B, et al. Effectiveness of establishing a dedicated acute stroke unit in routine clinical practice in Israel. Israel Medical Association Journal 2005;7:688‐93. - PubMed
-
- Koton S, Schwammenthal Y, Merzeliak O, Philips T, Tsabari R, Bruk B, et al. Management and outcome of acute stroke: differences between organised short‐term acute stroke unit and general medical wards. Cerebrovacular Diseases 2005;19 Suppl 2:58.
Langhorne 2001 {published data only}
-
- Langhorne P, Fraser P, Wright F, Shields M, MacIntosh G, Stott D. Evaluation of an acute care protocol for stroke patients: a controlled clinical trial. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2001;11 Suppl 4:35.
Middleton 2006 {published data only}
-
- Middelton S. An outcomes approach to stroke care; the importance of teamwork and evidence‐based nursing care. International Journal of Stroke 2012;7:224‐6. - PubMed
-
- Middleton S, Levi C, Griffiths R, Grimshaw J, Ward J. Quality in Acute Stroke Care project: protocol for a cluster randomised control trial to evaluate the management of fever, sugar and swallowing after stroke. Journal of Internal Medicine 2006;36:A1‐A14.
-
- Middleton S, McElduff P, Ward J, Grimshaw J, Dale S, D'Este C, et al. Implementation of evidence‐based treatment protocols to manage fever, hyperglycaemia and swallowing dysfunction in acute stroke (QASC): a cluster randomised control trial. Lancet 2011;378:1699‐706. - PubMed
Moloney 1999 {published data only}
-
- Moloney A, Critchlow B, Jones K. A multi‐disciplinary care pathway in stroke ‐ does it improve care?. Age and Ageing 1999;28 Suppl 1:42‐3.
Pappa 2009 {published data only}
-
- Pappa T, Spengos K, Skoufi M, Zafiriou I, Barbaressou Z, Peppa K, et al. Acute stroke unit improves long‐term survival in very old stroke patients. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2009;27 Suppl 6:13.
Patel 2000 {unpublished data only}
-
- Patel N, Louw S, Zwarenstein M. Organised care of acute stroke at Groot Schuur Hospital (MPhil in Epidemiology). Cape Town: University of Cape Town, 2000.
Pearson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Pearson A, Durand I, Punton S. Effects of admission to a nursing unit. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing 1988;6(1):38‐42. - PubMed
Ricauda 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ricauda NA, Bo M, Molaschi M, Massaia M, Salerno D, Amati D, et al. Home hospitalization service for acute uncomplicated first ischemic stroke in elderly patients: a randomized trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2004;52:278‐83. - PubMed
Ronning 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Ronning OM, Guldvog B. Stroke units versus general medical wards, II: neurological deficits and activities of daily living: a quasi‐randomised controlled trial. Stroke 1998;29:586‐90. - PubMed
-
- Stavem K, Ronning OM. Survival over 12 years following acute stroke: initial treatment in a stroke unit versus general medical ward. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2011;124(6):429‐433. - PubMed
Ronning 1998a {published data only}
-
- Ronning OM, Guldvog B. Stroke units versus general medical wards, I: twelve‐ and eighteen‐month survival. A randomized controlled trial. Stroke 1998;29:58‐62. - PubMed
Ronning 1998b {published data only}
-
- Ronning OM, Guldvog B. Outcome of subacute stroke rehabilitation. A randomized controlled trial. Stroke 1998;29:779‐84. - PubMed
Shiraishi 2004 {published data only}
-
- Shirashi N, Mizutani C, Menjho M, Deguchi A, Takase K, Hamaguchi H, et al. Comparison of daily living for a convalescent rehabilitation ward and general ward for stroke patients. Japanese Journal of Geriatrics 2004;41:646‐52. - PubMed
Silva 2004 {published data only}
-
- Silva Y, Piugdemont M, Castellanos M, Serena J, Suner RM, Davalos A. Semi‐intensive monitoring in acute stroke and long term outcome. Stroke 2002; Vol. 33, issue 1:411. - PubMed
-
- Silva Y, Puigdemont M, Castellanos M, Serena J, Suner RM, Garcia MM, et al. Semi‐intensive monitoring in acute stroke and long term outcome. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;19(1):23‐30. - PubMed
-
- Silva Y, Serena J, Castellanos M, Ramio L, Osuna T, Davalos A. Stroke units: the effect of continuous monitoring on clinical outcome. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2001;11 Suppl 4:122.
Stone 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Stone SP. A trial of stroke unit (SU) versus comprehensive geriatric service (CGS) management of all stroke patients. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 1999;13(1):13.
Strand 1985 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Strand T, Asplund K, Eriksson S, Hagg E, Lithner F, Wester PO. A non‐intensive stroke unit reduced functional disability and the need for long‐term hospitalisation. Stroke 1985;16:29‐34. - PubMed
-
- Strand T, Asplund K, Eriksson S, Hagg E, Lithner F, Wester PO. Stroke unit care ‐ who benefits? Comparisons with general medical care in relation to prognostic indicators on admission. Stroke 1986;17:377‐81. - PubMed
von Arbin 1980 {published data only}
-
- Arbin M, Britton M, Faire U, Helmers C, Miah K, Murray V. A study of stroke patients treated in a non‐intensive stroke unit or in general medical wards. Acta Medica Scandinavica 1980;208:81‐5. - PubMed
Walter 2005 {published data only}
-
- Walter A, Seidel G, Thie A, Raspe HH, for the SSSH Study Group. German stroke units versus conventional care in acute ischemic stroke and TIA ‐ a prospective study. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;19 Suppl 2:30.
Wang 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wang YJ, Gao XL, Ma RH, Wu D. Beijing Organized Stroke Care Study (BOSS). Proceedings of the 29th International Stroke Conference, San Diego, California, USA. 5‐7 February 2004.
Yagura 2005 {published data only}
-
- Yagura H, Miyai I, Suzuki T, Yanagihara T. Patients with severe stroke benefit most by interdisciplinary rehabilitation team approach. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2005;20:258‐63. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Anhui 2008 {published data only}
-
- Ni C, Li C, Han R, Chen J, Sun H, Liu S. A randomised controlled trial of standardised tertiary rehabilitation after stroke. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008;Suppl 46:71.
China (Hao) 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hao JJ. Effect of comprehensive stroke unit on patients with pneumonia after acute stroke. Chinese Journal of Cerebrovascular Diseases 2010;7:120‐3.
China (Pei) 2011 {published data only}
-
- Pei Z. Clinical research of organised stroke care model with integrated Chinese traditional and Western medicine in primary hospital. Chinese Journal of Contemporary Neurology and Neurosurgery 2011;11:221‐5.
China (Wang) 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang ZM, Wang P, Chen J, Luo DH, Shen WM. Application of stroke rehabilitation in municipal hospitals during the acute phase of cerebral infarction. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology 2008;29:724‐5. - PubMed
China (Wu) 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wu WL, Lu XL, Zheng MY, Liang W, Yao XL, Hu ZL. Imapct of organised stroke unit on the therapeutic effect in stroke patients. Journal of Southern Medical University 2010;30:555‐6. - PubMed
Haikou 2007 {published data only}
-
- Su Q, Lin T, Wu Y, Cai M, Chen Z. Benefit of an extended stroke unit to acute cerebral infarction. Cerebrovascular Diseases 2007;24:490.
Shanghai 2006 {published data only}
-
- Hu YS. Standardized tertiary rehabilitation (STR) for stroke patients with hemiplegia in promoting the neurological function. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2006;20:163.
-
- Hu YS. Standarized tertiary rehabilitation (STR) for patients with cerebral strokes accompanied by hemiplegia. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2006;20:163.
-
- Jiang CY, Hu YS, Wang Q, Wu Y, Zhu YL. The cost‐effectiveness analysis of early rehabilitation for stroke patients. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2006;20:205.
-
- Sun LM, Hu YS, Wu Y, Zhu YL, Fan WK. Effect of standardized tertiary rehabilitation on the motor function in patients with cerebral stroke accompanied by hemiplegia. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair 2006;20:163.
References to ongoing studies
Baden 2007 {unpublished data only}
-
- Structured stroke management improves outcomes at 6 months. Ongoing study ‐.
Beijing 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Efficiency study of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) versus western medicine (WM) on ischaemic stroke. Ongoing study ‐.
Shanghai 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- A study of the stroke unit of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of ischaemic stroke. Ongoing study ‐.
Additional references
Barer 1993
-
- Barer D, Gibson OP, Ellul J and the "GUESS" Group. Outcome of hospital care for stroke in 12 centres. Proceedings of the British Geriatrics Society, Spring Meeting, Glasgow. April 15‐17, 1993.
Ebrahim 1990
-
- Ebrahim S. Clinical Epidemiology of Stroke. 1st Edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press (Medical Publications), 1990.
Garraway 1985
-
- Garraway WM. Stroke rehabilitation units: concepts, evaluation, and unresolved issues. Stroke 1985;16:178‐81. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Langhorne 2012
-
- Langhorne P, Villiers L, Pandian JD. Applicability of stroke‐unit care to low‐income and middle‐income countries. Lancet Neurology 2012;11:341‐48. - PubMed
Lozano 2012
Murray 2012
-
- Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, Naghavi M, Flaxman AD, Michaud C, et al. Disability‐adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380:2197‐223. - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.2. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Seenan 2007
-
- Seenan P, Long M, Langhorne P. Stroke units in their natural habitat: a systematic review of observational studies. Stroke 2007;38:1886‐92. - PubMed
Strong 2007
-
- Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurology 2007;6:182‐7. - PubMed
Wade 1992
-
- Wade D. Measurement in Neurological Rehabilitation. 1st Edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1992.
Warlow 2008
-
- Warlow C, Gijn J, Dennis M, Wardlaw J, Bamford J, Hankey G, et al. Stroke: Practical Management. 3rd Edition. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2008.
References to other published versions of this review
Langhorne 1993
-
- Langhorne P, Williams BO, Gilchrist W, Howie K. Do stroke units save lives?. Lancet 1993;342:395‐8. - PubMed
Langhorne 1998
-
- Langhorne P, Dennis MS, on behalf of the Stroke Unit Trialists' Collaboration. Stroke Units: An Evidence Based Approach. London: BMJ Books, 1998.
Major 1998
-
- Major K, Walker A. Economics of stroke unit care. In: Langhorne P, Dennis MS editor(s). Stroke Units: An Evidence Based Approach. London: BMJ Books, 1998.
SUTC 1997a
SUTC 1997b
-
- Stroke Unit Trialists' Collaboration. How do stroke units improve patient outcomes? A collaborative systematic review of the randomized trials. Stroke 1997;28:2139‐44. - PubMed
SUTC 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

