IL-9 and Th9 cells: progress and challenges
- PMID: 24027199
- PMCID: PMC3784066
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxt039
IL-9 and Th9 cells: progress and challenges
Abstract
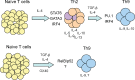
T(h)9 cells are a new subset of helper T cells, and the signature cytokine for T(h)9 cells is IL-9. Both T(h)9 cells and T(h)9 products are implicated in multiple disease settings. Thus, a clear understanding of how T(h)9 cells are induced and controlled is an important and clinically relevant issue. There are different molecular pathways identified thus far in the induction of T(h)9 cells, and activation of such diverse pathways requires integration of signals from TGF-β and IL-4 cytokine receptors as well as costimulatory molecules. These signals converge on the induction of multiple transcription factors that collectively drive the development of T(h)9 cells.
Keywords: IL-9; Th9; allergy; inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TH9 cells are required for tissue mast cell accumulation during allergic inflammation.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Aug;136(2):433-40.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.021. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25746972 Free PMC article.
-
Th9 cells, new players in adaptive immunity.Trends Immunol. 2014 Feb;35(2):61-8. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Trends Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24215739 Review.
-
Th9 cells and IL-9 in autoimmune disorders: Pathogenesis and therapeutic potentials.Hum Immunol. 2017 Feb;78(2):120-128. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2016.12.010. Epub 2016 Dec 28. Hum Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28040536 Review.
-
Th9 Cells: Probable players in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis.Int Rev Immunol. 2018;37(4):192-205. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2018.1457659. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Int Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29672174
-
Th9 and other IL-9-producing cells in allergic asthma.Semin Immunopathol. 2017 Jan;39(1):55-68. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0601-1. Epub 2016 Nov 17. Semin Immunopathol. 2017. PMID: 27858144 Review.
Cited by
-
T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.Cytokine. 2015 Jul;74(1):5-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Cytokine. 2015. PMID: 25458968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 promotes T helper type 17 differentiation by promoting interleukin-9 production.Immunology. 2020 Aug;160(4):357-365. doi: 10.1111/imm.13199. Epub 2020 May 8. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32277469 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of IL-9 producing T cells in the PBMCs of allergic asthmatic patients.BMC Immunol. 2017 Jul 19;18(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12865-017-0220-1. BMC Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28724400 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of Th9 cells and their potential role in immunopathogenesis of murine schistosomiasis.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Jun 24;10(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2242-1. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28646920 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell receptor variable region usage in Chagas disease: A systematic review of experimental and human studies.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Sep 15;16(9):e0010546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010546. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36107855 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li X. C., Schachter A. D., Zand M. S., et al. 1998. Differential expression of T-cell growth factors in rejecting murine islet and human renal allografts: conspicuous absence of interleukin (IL)-9 despite expression of IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, and IL-15. Transplantation 66:265. - PubMed
-
- Knoops L., Renauld J. C. 2004. IL-9 and its receptor: from signal transduction to tumorigenesis. Growth Factors 22:207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

