Presenilins regulate the cellular activity of ryanodine receptors differentially through isotype-specific N-terminal cysteines
- PMID: 24029002
- PMCID: PMC3843983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.09.001
Presenilins regulate the cellular activity of ryanodine receptors differentially through isotype-specific N-terminal cysteines
Abstract
Presenilins (PS), endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane proteins, form the catalytic core of γ-secretase, an amyloid precursor protein processing enzyme. Mutations in PS lead to Alzheimer's disease (AD) by altering γ-secretase activity to generate pathologic amyloid beta and amyloid plaques in the brain. Here, we identified a novel mechanism where binding of a soluble, cytosolic N-terminal domain fragment (NTF) of PS to intracellular Ca(2+) release channels, ryanodine receptors (RyR), controls Ca(2+) release from the ER. While PS1NTF decreased total RyR-mediated Ca(2+) release, PS2NTF had no effect at physiological Ca(2+) concentrations. This differential function and isotype-specificity is due to four cysteines absent in PS1NTF, present, however, in PS2NTF. Site-directed mutagenesis targeting these cysteines converted PS1NTF to PS2NTF function and vice versa, indicating differential RyR binding. This novel mechanism of intracellular Ca(2+) regulation through the PS-RyR interaction represents a novel target for AD drug development and the treatment of other neurodegenerative disorders that critically depend on RyR and PS signaling.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Endoplasmic reticulum; Intracellular calcium; Neuroprotection; Oxidative stress.
© 2013.
Figures

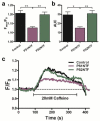
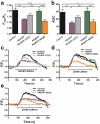

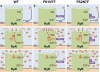
References
-
- Alzheimer's Association 2012 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8:131–168. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer's Disease Collaborative Group The structure of the presenilin 1 (S182) gene and identification of six novel mutations in early onset AD families. Alzheimer's Disease Collaborative Group. Nat Genet. 1995;11:219–222. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, Lee MK, Davenport F, Ratovitsky T, Prada CM, Kim G, Seekins S, Yager D, Slunt HH, Wang R, Seeger M, Levey AI, Gandy SE, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Price DL, Younkin SG, Sisodia SS. Familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Abeta1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron. 1996;17:1005–1013. - PubMed
-
- Borghi R, Piccini A, Barini E, Cirmena G, Guglielmotto M, Tamagno E, Fornaro M, Perry G, Smith MA, Garuti A, Tabaton M. Upregulation of presenilin 1 in brains of sporadic, late-onset Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;22(3):771–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AG022550/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG027956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG022550/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG010485/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- EY022774/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- RR022570/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR027093/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AG010485/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY014227/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY014227/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY022774/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- AG027956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027093/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR022570/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

