Prediction of outcomes in crescentic IgA nephropathy in a multicenter cohort study
- PMID: 24029421
- PMCID: PMC3839544
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012101017
Prediction of outcomes in crescentic IgA nephropathy in a multicenter cohort study
Abstract
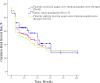
Crescentic IgA nephropathy (IgAN), defined as >50% crescentic glomeruli on kidney biopsy, is one of the most common causes of rapidly progressive GN. However, few studies have characterized this condition. To identify risk factors and develop a prediction model, we assessed data from patients ≥ 14 years old with crescentic IgAN who were followed ≥ 12 months. The discovery cohort comprised 52 patients from one kidney center, and the validation cohort comprised 61 patients from multiple centers. At biopsy, the mean serum creatinine (SCr) level ± SD was 4.3 ± 3.4 mg/dl, and the mean percentage of crescents was 66.4%± 15.8%. The kidney survival rates at years 1, 3, and 5 after biopsy were 57.4%± 4.7%, 45.8%± 5.1%, and 30.4%± 6.6%, respectively. Multivariate Cox regression revealed initial SCr as the only independent risk factor for ESRD (hazard ratio [HR], 1.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.10 to 1.57; P=0.002). Notably, the percentage of crescents did not associate independently with ESRD. Logistic regression showed that the risk of ESRD at 1 year after biopsy increased rapidly at SCr>2.7 mg/dl and reached 90% at SCr>6.8 mg/dl (specificity=98.5%, sensitivity=64.6% for combined cohorts). In both cohorts, patients with SCr>6.8 mg/dl were less likely to recover from dialysis. Analyses in additional cohorts revealed a similar association between initial SCr and ESRD in patients with antiglomerular basement membrane disease but not ANCA-associated systemic vasculitis. In conclusion, crescentic IgAN has a poor prognosis, and initial SCr concentration may predict kidney failure in patients with this disease.
Figures


References
-
- D’Amico G: Natural history of idiopathic IgA nephropathy and factors predictive of disease outcome. Semin Nephrol 24: 179–196, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Roberts IS, Cook HT, Troyanov S, Alpers CE, Amore A, Barratt J, Berthoux F, Bonsib S, Bruijn JA, Cattran DC, Coppo R, D’Agati V, D’Amico G, Emancipator S, Emma F, Feehally J, Ferrario F, Fervenza FC, Florquin S, Fogo A, Geddes CC, Groene HJ, Haas M, Herzenberg AM, Hill PA, Hogg RJ, Hsu SI, Jennette JC, Joh K, Julian BA, Kawamura T, Lai FM, Li LS, Li PK, Liu ZH, Mackinnon B, Mezzano S, Schena FP, Tomino Y, Walker PD, Wang H, Weening JJ, Yoshikawa N, Zhang H, Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society : The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: Pathology definitions, correlations, and reproducibility. Kidney Int 76: 546–556, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Barratt J, Feehally J: IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 16: 2088–2097, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Abe T, Kida H, Yoshimura M, Yokoyama H, Koshino Y, Tomosugi N, Hattori N: Participation of extracapillary lesions (ECL) in progression of IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 25: 37–41, 1986 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

