The E1 proteins
- PMID: 24029589
- PMCID: PMC3811109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2013.07.020
The E1 proteins
Abstract
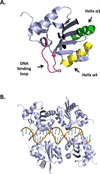
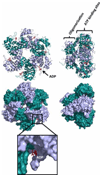
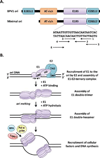
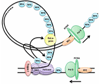
E1, an ATP-dependent DNA helicase, is the only enzyme encoded by papillomaviruses (PVs). It is essential for replication and amplification of the viral episome in the nucleus of infected cells. To do so, E1 assembles into a double-hexamer at the viral origin, unwinds DNA at the origin and ahead of the replication fork and interacts with cellular DNA replication factors. Biochemical and structural studies have revealed the assembly pathway of E1 at the origin and how the enzyme unwinds DNA using a spiral escalator mechanism. E1 is tightly regulated in vivo, in particular by post-translational modifications that restrict its accumulation in the nucleus. Here we review how different functional domains of E1 orchestrate viral DNA replication, with an emphasis on their interactions with substrate DNA, host DNA replication factors and modifying enzymes. These studies have made E1 one of the best characterized helicases and provided unique insights on how PVs usurp different host-cell machineries to replicate and amplify their genome in a tightly controlled manner.
Keywords: ATPase; DNA replication; E1; Episome; Helicase; Papillomavirus; Phosphoryaltion; Post-translational modifications.
© 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Amin AA, Titolo S, Pelletier A, Fink D, Cordingley MG, Archambault J. Identification of domains of the HPV11 E1 protein required for DNA replication in vitro. Virology. 2000;272:137–150. - PubMed
-
- Auster AS, Joshua-Tor L. The DNA-binding domain of human papillomavirus type 18 E1. Crystal structure, dimerization, and DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:3733–3742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

