Inflammation-mediated skin tumorigenesis induced by epidermal c-Fos
- PMID: 24029918
- PMCID: PMC3792473
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.223339.113
Inflammation-mediated skin tumorigenesis induced by epidermal c-Fos
Abstract
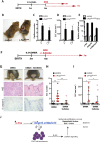
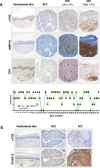
Skin squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) are the second most prevalent skin cancers. Chronic skin inflammation has been associated with the development of SCCs, but the contribution of skin inflammation to SCC development remains largely unknown. In this study, we demonstrate that inducible expression of c-fos in the epidermis of adult mice is sufficient to promote inflammation-mediated epidermal hyperplasia, leading to the development of preneoplastic lesions. Interestingly, c-Fos transcriptionally controls mmp10 and s100a7a15 expression in keratinocytes, subsequently leading to CD4 T-cell recruitment to the skin, thereby promoting epidermal hyperplasia that is likely induced by CD4 T-cell-derived IL-22. Combining inducible c-fos expression in the epidermis with a single dose of the carcinogen 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene (DMBA) leads to the development of highly invasive SCCs, which are prevented by using the anti-inflammatory drug sulindac. Moreover, human SCCs display a correlation between c-FOS expression and elevated levels of MMP10 and S100A15 proteins as well as CD4 T-cell infiltration. Our studies demonstrate a bidirectional cross-talk between premalignant keratinocytes and infiltrating CD4 T cells in SCC development. Therefore, targeting inflammation along with the newly identified targets, such as MMP10 and S100A15, represents promising therapeutic strategies to treat SCCs.
Keywords: AP-1; CD4 T cell; c-Fos; cancer; inflammation; skin.
Figures
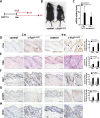
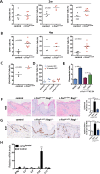
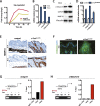
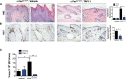
References
-
- Aikawa Y, Morimoto K, Yamamoto T, Chaki H, Hashiramoto A, Narita H, Hirono S, Shiozawa S 2008. Treatment of arthritis with a selective inhibitor of c-Fos/activator protein-1. Nat Biotechnol 26: 817–823 - PubMed
-
- Baldursson B, Sigurgeirsson B, Lindelof B 1993. Leg ulcers and squamous cell carcinoma. An epidemiological study and a review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol 73: 171–174 - PubMed
-
- Barksby HE, Milner JM, Patterson AM, Peake NJ, Hui W, Robson T, Lakey R, Middleton J, Cawston TE, Richards CD, et al. 2006. Matrix metalloproteinase 10 promotion of collagenolysis via procollagenase activation: Implications for cartilage degradation in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54: 3244–3253 - PubMed
-
- Boniface K, Bernard FX, Garcia M, Gurney AL, Lecron JC, Morel F 2005. IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol 174: 3695–3702 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
