Holiday heart syndrome revisited after 34 years
- PMID: 24030078
- PMCID: PMC3998158
- DOI: 10.5935/abc.20130153
Holiday heart syndrome revisited after 34 years
Abstract
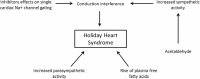
The cardiovascular effects of alcohol are well known. However, most research has focused on the beneficial effects (the "French paradox") of moderate consumption or the harmful consequences, such as dilated cardiomyopathy, associated with heavy consumption over an extended period. An association between the ingestion of acute alcohol and onset of cardiac arrhythmias was first reported in the early 70's. In 1978, Philip Ettinger described "Holiday heart syndrome" (HHS) for the first time, as the occurrence, in healthy people without heart disease known to cause arrhythmia, of an acute cardiac rhythm disturbance, most frequently atrial fibrillation, after binge drinking. The name is derived from the fact that episodes were initially observed more frequently after weekends or public holidays. Since the original description of HHS, 34 years have passed and new research in this field has increased the volume of knowledge related to this syndrome. Throughout this paper the authors will comprehensively review most of the available data concerning HHS and highlight the questions that remain unresolved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- National Council on Alcoholism and Drug Dependence, Inc. [Cited in 2012 Sep 5]. Available from: http://www.ncadd.org/index.php/learn-about-alcohol/faqsfacts.
-
- Providencia R. Protecção cardiovascular por bebidas alcoólicas: bases científicas do paradoxo francês. RevPortCardiol. 2006;25(11):1043–1058.
-
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism [Cited in 2012 Sep 5]. Available from: http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/alcohols-effects-body.
-
- Djoussé L, Levy D, Benjamin EJ, Blease SJ, Russ A, Larson MG, et al. Long-term alcohol consumption and the risk of atrial fibrillation in the Framingham Study. Am J Cardiol. 2004;93(6):710–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical