Delta-opioid receptors attenuate TNF-α-induced MMP-2 secretion from human ONH astrocytes
- PMID: 24030463
- PMCID: PMC3803137
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.13-12196
Delta-opioid receptors attenuate TNF-α-induced MMP-2 secretion from human ONH astrocytes
Abstract
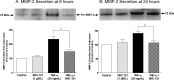
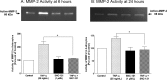
Purpose: We examined the signaling mechanisms involved in δ-opioid-receptor agonist, SNC-121-mediated attenuation of TNF-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) secretion from human optic nerve head (ONH) astrocytes.
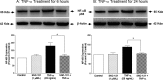
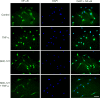
Methods: Human ONH astrocytes were treated with SNC-121 (1 μmol/L) for 15 minutes followed by TNF-α (25 ng/mL) treatment for 6 or 24 hours. Cells were pretreated with inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase (SB-203580) or NF-κB (Helenalin) prior to TNF-α treatment. Changes in phosphorylation and expression of p38 MAP kinase, IκBα, NF-κB, and MMP-2 were measured by Western blotting. Translocation of NF-κB was determined by immunocytochemistry.
Results: TNF-α treatment increased MMP-2 secretion from ONH astrocytes to 236% ± 17% and 142% ± 8% at 6 and 24 hours, respectively; while SNC-121 treatment reduced MMP-2 secretion to 149% ± 11% and 108% ± 7% at 6 and 24 hours, respectively. The SNC-121-mediated inhibitory response was blocked by the δ-opioid-receptor antagonist naltrindole. TNF-α treatment resulted in a sustained phosphorylation of p38 MAP kinase up to 24 hours (226% ± 15% over control levels), which was reduced to 150% ± 20% by SNC-121 treatment. TNF-α treatment increased the expression of NF-κB to 179% ± 21% and 139% ± 6% at 6 and 24 hours, respectively, which was significantly blocked by SNC-121 treatment. Furthermore, TNF-α-induced MMP-2 secretion was blocked by 100% and 78% in the presence of SB-203580 and Helenalin, respectively.
Conclusions: Evidence is provided that SNC-121 attenuated TNF-α-induced MMP-2 secretion from ONH astrocytes. Data also supported the idea that p38 MAP kinase and NF-κB played central roles in TNF-α-induced MMP-2 secretion, and both were negatively regulated by SNC-121.
Keywords: astrocytes; glaucoma; matrix metalloproteinases; opioids; optic nerve head.
Figures




References
-
- Hernandez MR. The optic nerve head in glaucoma: role of astrocytes in tissue remodeling. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2000; 19: 297– 321 - PubMed
-
- Hernandez MR, Pena JD. The optic nerve head in glaucomatous optic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997; 115: 389– 395 - PubMed
-
- Morrison JC, Dorman-Pease ME, Dunkelberger GR, Quigley HA. Optic nerve head extracellular matrix in primary optic atrophy and experimental glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108: 1020– 1024 - PubMed
-
- Toft-Hansen H, Fuchtbauer L, Owens T. Inhibition of reactive astrocytosis in established experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis favors infiltration by myeloid cells over T cells and enhances severity of disease. Glia. 2011; 59: 166– 176 - PubMed
-
- Woessner JF Jr. Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991; 5: 2145– 2154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

