Production and characterization of PHA from recombinant E. coli harbouring phaC1 gene of indigenous Pseudomonas sp. LDC-5 using molasses
- PMID: 24031729
- PMCID: PMC3768782
- DOI: 10.1590/S1517-838220110003000032
Production and characterization of PHA from recombinant E. coli harbouring phaC1 gene of indigenous Pseudomonas sp. LDC-5 using molasses
Abstract
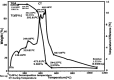
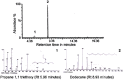
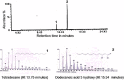
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) are biodegradable and biocompatible green thermoplastics, synthesized by wide variety of bacteria as an intracellular carbon and energy storage intermediate. They are used as an alternative to nonrenewable petroleum derived plastics. The current interest in these biopolyesters is stimulated by the search for cost-effective capitalized production. This paper attempts to achieve maximized production rate from recombinant system using inexpensive substrate. Molasses from agro-industrial waste was used to produce PHA from recombinant E.coli in batch culture. PHA yield in molasses (3.06g/L ± 0.05‒75.5%) was higher than that of sucrose (2.5g/L ± 0.05 - 65.1%). Properties of the polymer produced from molasses and sucrose were analyzed by DSC, TGA, DTA, GC/MS, TLC and optical rotation studies. The findings suggested that molasses enhanced PHA production in recombinant E.coli.
Keywords: Polyhydroxyalkanoates; cost effective production; molasses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of nutritional supplements on bio-plastics (PHB) production utilizing sugar refinery waste with potential application in food packaging.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2019;49(6):567-577. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2019.1591982. Epub 2019 Mar 31. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30929621
-
Bacterial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using various waste carbon sources.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 24;12:e17936. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17936. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39465164 Free PMC article.
-
A study on medium chain length-polyhydroxyalkanoate accumulation in Escherichia coli harbouring phaC1 gene of indigenous Pseudomonas sp. LDC-5.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006 Dec;43(6):607-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2006.02016.x. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17083705
-
[The degradation of plastics and the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA)].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 May 25;39(5):2053-2069. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.230033. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37212231 Review. Chinese.
-
A comprehensive overview and recent advances on polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production using various organic waste streams.Bioresour Technol. 2021 Apr;325:124685. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.124685. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Bioresour Technol. 2021. PMID: 33508681 Review.
Cited by
-
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable resources: a review on prospects, challenges and applications.Arch Microbiol. 2023 Apr 5;205(5):172. doi: 10.1007/s00203-023-03499-8. Arch Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37017747 Review.
-
Biodegradation Studies of Polyhydroxybutyrate and Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-Polyhydroxyvalerate Films in Soil.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 21;24(8):7638. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087638. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108799 Free PMC article.
-
A Polyhydroxyalkanoates-Based Carrier Platform of Bioactive Substances for Therapeutic Applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 5;9:798724. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.798724. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35071207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of microbial resources in biorefineries: Current trend and future prospects.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 27;10(8):e28615. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28615. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38628756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trends in PHA Production by Microbially Diverse and Functionally Distinct Communities.Microb Ecol. 2023 Feb;85(2):572-585. doi: 10.1007/s00248-022-01995-w. Epub 2022 Mar 25. Microb Ecol. 2023. PMID: 35333950 Review.
References
-
- Dawes E.A., Senior P.J. The role and regulation of energy reserve polymers in microorganisms. Adv Micro Physiol. 1973;10:135–266. - PubMed
-
- De Campos A., Franchetti S.M.M., Agnelli J.A.M. Biotransformation of poly (epsilon-caprolactone) and poly (vinyl chloride) blend. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2003;34(1):111–113.
-
- Doi Y., Kitamura S., Abe H. Microbial synthesis and characterization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) Macromol. 1995;28:4822–4828.
-
- Eggink G., Northolt M.D. Method for producing a biologically degradable Polyhydroxyalkanoates coating with the aid of an aqueous dispersion of Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Polymer. 1995;42:3296–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
