Thermostability of xylanolytic enzymes produced by Lentinula edodes UFV70
- PMID: 24031818
- PMCID: PMC3768989
- DOI: 10.1590/S1517-838220120001000021
Thermostability of xylanolytic enzymes produced by Lentinula edodes UFV70
Abstract
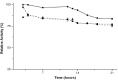
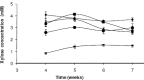
Xylanolytic enzymes produced by Lentinula edodes UFV70, cultivated in eucalyptus sawdust/rice bran medium, were stable at 50, 60 and 65°C for 21 hours, losing only 15-25% activity. Fungus incubation at 50°C for 12 hours and at 65°C for 24 hours increased the amount of xylose produced.
Keywords: Lentinula edodes; thermostability; xylanase; xylose.
Figures
References
-
- Bradford M.M. A dye binding assay for protein. Anal. Biochem. 1976;72:248–9. 254. - PubMed
-
- Cavallazzi J.R.P.O., Almeida M.G., Kasuya M.C.M. Laccase production by Lepista sordida. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2004;35:261–263.
-
- Elisashvili V.P., H., Kachlishvili E., Chichua D., Bakradze M., Kohreidze N. Ligninolytic activity of basidiomycetes grown under submerged and solid-state fermentation on plant raw material (sawdust of grapevine cuttings) Adv. Food. Sci. 2001;23:117–123.
-
- Elisashvili V., Penninckx M., Kachlishvili E., Tsiklauri N., Metreveli E., Kharziania T., Kvesitadze G. Lentinus edodes and Pleurotus species lignocellulolytic enzymes activity in submerged and solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic wastes of different composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2007;99:457–462. - PubMed
-
- Haki G.D., Rakshit S.K. Developments in industrially important thermostable enzymes: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 2003;89:17–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
