Tuftsin signals through its receptor neuropilin-1 via the transforming growth factor beta pathway
- PMID: 24033337
- PMCID: PMC3805743
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12404
Tuftsin signals through its receptor neuropilin-1 via the transforming growth factor beta pathway
Abstract
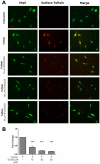
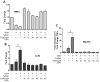
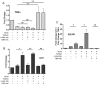
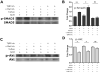
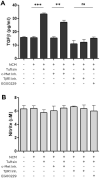
Tuftsin (Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg) is a natural immunomodulating peptide found to stimulate phagocytosis in macrophages/microglia. Tuftsin binds to the receptor neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) on the surface of cells. Nrp1 is a single-pass transmembrane protein, but its intracellular C-terminal domain is too small to signal independently. Instead, it associates with a variety of coreceptors. Despite its long history, the pathway through which tuftsin signals has not been described. To investigate this question, we employed various inhibitors to Nrp1's coreceptors to determine which route is responsible for tuftsin signaling. We use the inhibitor EG00229, which prevents tuftsin binding to Nrp1 on the surface of microglia and reverses the anti-inflammatory M2 shift induced by tuftsin. Furthermore, we demonstrate that blockade of transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling via TβR1 disrupts the M2 shift similar to EG00229. We report that tuftsin promotes Smad3 phosphorylation and reduces Akt phosphorylation. Taken together, our data show that tuftsin signals through Nrp1 and the canonical TGFβ signaling pathway. Despite the 40-year history of the tetrapeptide tuftsin (TKPR), a macrophage and microglial activator, its mechanism of action has not been defined. Here, we report that the tuftsin-mediated anti-inflammatory M2 shift in microglia is caused specifically by tuftsin binding to the receptor neuropilin-1 (Nrp1) and signaling through TGFβ receptor-1, a coreceptor of Nrp1. We further show that tuftsin signals via the canonical TGFβ pathway and promotes TGFβ release from target cells.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; cytokines; microglia; neuropilin 1; tuftsin.
© 2013 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

