In silico analysis and experimental validation of molecular mechanisms of salvianolic acid A-inhibited LPS-stimulated inflammation, in RAW264.7 macrophages
- PMID: 24033467
- PMCID: PMC6496881
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12056
In silico analysis and experimental validation of molecular mechanisms of salvianolic acid A-inhibited LPS-stimulated inflammation, in RAW264.7 macrophages
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study was to explore mechanisms by which salvianolic acid A (SAA) revealed its anti-inflammatory activity, in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells.
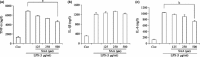
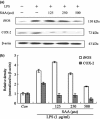
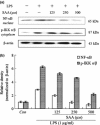
Materials and methods: Nitric oxide (NO) concentration was determined by the Griess reaction and cell viability was assessed by MTT assay. Interleukin-6, TNFα and interleukin-1β were determined by ELISA. The RAW264.7 cells were transfected with siRNA against p38 or HO-1. Expressions of COX-2, inducible NO synthase (iNOS), NF-κB, HO-1, p-p38 and phosphorylation of IκB kinase α/β were detected by western blotting. Potential targets of SAA were analysed by homology modelling, target prediction, protein-protein interaction prediction and docking studies.
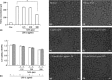
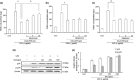
Results: Salvianolic acid A suppressed LPS-triggered production of NO, TNFα and Interleukin-6. It also reduced protein expression of inducible NO synthase and COX-2, and reduced translocation of NF-κB to nuclei. Moreover, SAA promoted expression of phosphorylated p38, and downstream HO-1. Zn (II) protoporphyrin IX, a specific inhibitor of HO-1, or siRNA against HO-1 could effectively increase transfer of NF-κB. SAA was predicted to target amyloid-beta protein-like protein and arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, that could regulate p38 and HO-1.
Conclusions: In silico analysis and experimental validation together demonstrated that SAA exhibited its anti-inflammatory effect via the p38-HO-1 pathway in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, reduced transfer of NF-κB to the nuclei and thus reduced production of inflammatory mediators.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The p38 MAPK inhibitor JLU1124 inhibits the inflammatory response induced by lipopolysaccharide through the MAPK-NF-κB pathway in RAW264.7 macrophages.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Nov;17(3):785-92. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.09.001. Epub 2013 Sep 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24070708
-
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits nitric oxide production and nuclear factor-kappaB via heme oxygenase-1 expression in RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide.Free Radic Biol Med. 2006 Jul 1;41(1):106-19. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.03.021. Epub 2006 Apr 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2006. PMID: 16781459
-
The anti-inflammatory role of heme oxygenase-1 in lipopolysaccharide and cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide production in human periodontal ligament cells.J Periodontol. 2009 Dec;80(12):2045-55. doi: 10.1902/jop.2009.090145. J Periodontol. 2009. PMID: 19961388
-
Nepetoidin B, a Natural Product, Inhibits LPS-stimulated Nitric Oxide Production via Modulation of iNOS Mediated by NF-κB/MKP-5 Pathways.Phytother Res. 2017 Jul;31(7):1072-1077. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5828. Epub 2017 May 15. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28504466
-
Methyl-1-hydroxy-2-naphthoate, a novel naphthol derivative, inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in macrophages via suppression of NF-κB, JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.Inflamm Res. 2011 Sep;60(9):851-9. doi: 10.1007/s00011-011-0345-2. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Inflamm Res. 2011. PMID: 21667204
Cited by
-
Integrated network pharmacology analysis, molecular docking, LC-MS analysis and bioassays revealed the potential active ingredients and underlying mechanism of Scutellariae radix for COVID-19.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 15;13:988655. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.988655. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36186074 Free PMC article.
-
Salvianolic Acid A Has Anti-Osteoarthritis Effect In Vitro and In Vivo.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jun 3;11:682. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00682. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32581777 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Nrf2 Protein Modulator Salvianolic Acid A Alone or Combined with Metformin on Diabetes-associated Macrovascular and Renal Injury.J Biol Chem. 2016 Oct 14;291(42):22288-22301. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.712703. Epub 2016 Jul 14. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27417135 Free PMC article.
-
CEMTDD: The database for elucidating the relationships among herbs, compounds, targets and related diseases for Chinese ethnic minority traditional drugs.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 10;6(19):17675-84. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3789. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25970778 Free PMC article.
-
Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 May;39(5):802-824. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.193. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29698387 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lundberg IE (2000) The role of cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2, 216–224. - PubMed
-
- Adams DO, Hamilton TA (1984) The cell biology of macrophage activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2, 283–318. - PubMed
-
- Walsh LJ (2003) Mast cells and oral inflammation. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 14, 188–198. - PubMed
-
- Tilg H, Wilmer A, Vogel W, Herold M, Nolchen B, Judmaier G et al (1992) Serum levels of cytokines in chronic liver diseases. Gastroenterology 103, 264–274. - PubMed
-
- Coker RK, Laurent GJ (1998) Pulmonary fibrosis: cytokines in the balance. Eur. Respir. J. 11, 1218–1221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

