Design of a comprehensive Alzheimer's disease clinic and research center in Spain to meet critical patient and family needs
- PMID: 24035148
- PMCID: PMC3951687
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.03.006
Design of a comprehensive Alzheimer's disease clinic and research center in Spain to meet critical patient and family needs
Abstract
Objectives: Alzheimer's disease (AD) affects people worldwide, and the prevalence is increasing as the population ages. There is an international effort to understand the biology of AD to develop primary and secondary prevention strategies, and to develop effective therapeutic interventions for individuals who are already symptomatic. One of the critically important pieces of all national plans to address AD is the call for the development of service models to deliver quality, effective care based on the best evidence available.
Methods: We describe one type of care model developed by the Fundacio ACE, Institut Catala de Neurociencies Aplicades (Fundacio ACE, Barcelona, Spain) that integrates diagnosis, therapy, follow-up care, daycare, and a day hospital, and does so in the context of an active clinical research and educational program.
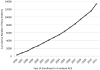
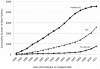
Results: There were 13,048 individuals newly evaluated and diagnosed in Fundacio ACE between 1996 and 2011. Of these, 6132 had AD (47.0%), 3871 had mild cognitive impairment (MCI) (29.7%), and 1958 had no cognitive impairment (15.0%). Follow-up information is available on 4735 (47.3%) AD and MCI patients, and these data indicate that MCI develops into dementia at a rate of 222.6/1000 person-years. Apolipoprotein E (APOE) genotyping was available in 22.4% of the patients. The ε4 allele occurred in 45.7% of the AD patients, in 37.8% of the MCI subjects, and in 31.6% of those without cognitive impairment.
Conclusions: Fundació ACE can serve as a model system that can be adapted to other settings within their specific cultural, governmental, and legal constraints.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Dementia; Natural history; Spain.
Copyright © 2014 The Alzheimer's Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2012 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2012;8(2):131–68. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International . World Alzheimer Report 2010: The global economic impact of dementia. London: 2010.
-
- Special Committee on Aging . Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: A Comparison of International Approaches: Report of the Special Committee on Aging, United States Senate, Pursuant to S. RES. 81, SEC. 17(d), March 2, 2011 Resolution Authorizing a Study of the Problems of Aged and Aging. 2011.
-
- Alzheimer Europe . National Dementia Plans: A snapshot of the status of National Dementia Strategies around Europe. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

