Adrenocortical zonation results from lineage conversion of differentiated zona glomerulosa cells
- PMID: 24035414
- PMCID: PMC3791142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.07.016
Adrenocortical zonation results from lineage conversion of differentiated zona glomerulosa cells
Abstract
Lineage conversion of differentiated cells in response to hormonal feedback has yet to be described. To investigate this, we studied the adrenal cortex, which is composed of functionally distinct concentric layers that develop postnatally, the outer zona glomerulosa (zG) and the inner zona fasciculata (zF). These layers have separate functions, are continuously renewed in response to physiological demands, and are regulated by discrete hormonal feedback loops. Their cellular origin, lineage relationship, and renewal mechanism, however, remain poorly understood. Cell-fate mapping and gene-deletion studies using zG-specific Cre expression demonstrate that differentiated zG cells undergo lineage conversion into zF cells. In addition, zG maintenance is dependent on the master transcriptional regulator Steroidogenic Factor 1 (SF-1), and zG-specific Sf-1 deletion prevents lineage conversion. These findings demonstrate that adrenocortical zonation and regeneration result from lineage conversion and may provide a paradigm for homeostatic cellular renewal in other tissues.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
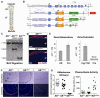
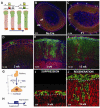
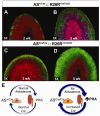
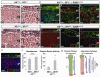
Comment in
-
Never underestimate the complexity of remodeling.Endocrinology. 2013 Dec;154(12):4446-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1982. Endocrinology. 2013. PMID: 24273232 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beuschlein F, Mutch C, Bavers DL, Ulrich-Lai YM, Engeland WC, Keegan C, Hammer GD. Steroidogenic factor-1 is essential for compensatory adrenal growth following unilateral adrenalectomy. Endocrinology. 2002;143:3122–3135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
