Proteasomes activate aggresome disassembly and clearance by producing unanchored ubiquitin chains
- PMID: 24035499
- PMCID: PMC3791850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.08.016
Proteasomes activate aggresome disassembly and clearance by producing unanchored ubiquitin chains
Abstract
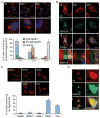
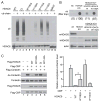
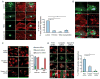
Aberrant protein aggregation is a dominant pathological feature in neurodegenerative diseases. Protein aggregates cannot be processed by the proteasome; instead, they are frequently concentrated to the aggresome, a perinuclear inclusion body, and subsequently removed by autophagy. Paradoxically, proteasomes are also concentrated at aggresomes and other related inclusion bodies prevalent in neurodegenerative disease. Here, we show that proteasomes are crucial components in aggresome clearance. The disassembly and disposal of aggresomes requires Poh1, a proteasomal deubiquitinating enzyme that cleaves ubiquitinated proteins and releases ubiquitin chains. In Poh1-deficient cells, aggresome clearance is blocked. Remarkably, microinjection of free lysine (K) 63-linked ubiquitin chains restores aggresome degradation. We present evidence that free ubiquitin chains produced by Poh1 bind and activate the deacetylase HDAC6, which, in turn, stimulates actinomyosin- and autophagy-dependent aggresome processing. Thus, unanchored ubiquitin chains are key signaling molecules that connect and coordinate the proteasome and autophagy to eliminate toxic protein aggregates.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bennett EJ, Shaler TA, Woodman B, Ryu KY, Zaitseva TS, Becker CH, Bates GP, Schulman H, Kopito RR. Global changes to the ubiquitin system in Huntington’s disease. Nature. 2007;448:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Gallery M, Blank JL, Lin Y, Gutierrez JA, Pulido JC, Rappoli D, Badola S, Rolfe M, Macbeth KJ. The JAMM motif of human deubiquitinase Poh1 is essential for cell viability. Molecular cancer therapeutics. 2007;6:262–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

