β-Adrenergic receptors activate exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), translocate Munc13-1, and enhance the Rab3A-RIM1α interaction to potentiate glutamate release at cerebrocortical nerve terminals
- PMID: 24036110
- PMCID: PMC3829451
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.463877
β-Adrenergic receptors activate exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), translocate Munc13-1, and enhance the Rab3A-RIM1α interaction to potentiate glutamate release at cerebrocortical nerve terminals
Abstract
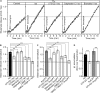
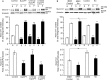
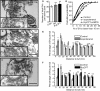
The adenylyl cyclase activator forskolin facilitates synaptic transmission presynaptically via cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). In addition, cAMP also increases glutamate release via PKA-independent mechanisms, although the downstream presynaptic targets remain largely unknown. Here, we describe the isolation of a PKA-independent component of glutamate release in cerebrocortical nerve terminals after blocking Na(+) channels with tetrodotoxin. We found that 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP, a specific activator of the exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac), mimicked and occluded forskolin-induced potentiation of glutamate release. This Epac-mediated increase in glutamate release was dependent on phospholipase C, and it increased the hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Moreover, the potentiation of glutamate release by Epac was independent of protein kinase C, although it was attenuated by the diacylglycerol-binding site antagonist calphostin C. Epac activation translocated the active zone protein Munc13-1 from soluble to particulate fractions; it increased the association between Rab3A and RIM1α and redistributed synaptic vesicles closer to the presynaptic membrane. Furthermore, these responses were mimicked by the β-adrenergic receptor (βAR) agonist isoproterenol, consistent with the immunoelectron microscopy and immunocytochemical data demonstrating presynaptic expression of βARs in a subset of glutamatergic synapses in the cerebral cortex. Based on these findings, we conclude that βARs couple to a cAMP/Epac/PLC/Munc13/Rab3/RIM-dependent pathway to enhance glutamate release at cerebrocortical nerve terminals.
Keywords: Cyclic AMP (cAMP); Epac Proteins; G Protein-coupled Receptors (GPCR); Munc13–1; Neurotransmitter Release; Phospholipase C; RIM1α; Rab3A; Synaptosomes.
Figures





Similar articles
-
β-Adrenergic Receptors/Epac Signaling Increases the Size of the Readily Releasable Pool of Synaptic Vesicles Required for Parallel Fiber LTP.J Neurosci. 2020 Nov 4;40(45):8604-8617. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0716-20.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 12. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33046543 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-talk between metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 and beta adrenergic receptor signaling at cerebrocortical nerve terminals.Neuropharmacology. 2016 Feb;101:412-25. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.07.025. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Neuropharmacology. 2016. PMID: 26211974
-
The loss of β adrenergic receptor mediated release potentiation in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Neurobiol Dis. 2019 Oct;130:104482. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104482. Epub 2019 May 23. Neurobiol Dis. 2019. PMID: 31129085
-
Epac-selective cAMP analogs: new tools with which to evaluate the signal transduction properties of cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factors.Cell Signal. 2008 Jan;20(1):10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 17716863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RIM function in short- and long-term synaptic plasticity.Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Dec;33(Pt 6):1345-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0331345. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005. PMID: 16246115 Review.
Cited by
-
Epac2 in midbrain dopamine neurons contributes to cocaine reinforcement via enhancement of dopamine release.Elife. 2022 Aug 22;11:e80747. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80747. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35993549 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of osteoclastogenesis via α2-adrenergic receptors.Biomed Rep. 2018 May;8(5):407-416. doi: 10.3892/br.2018.1075. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Biomed Rep. 2018. PMID: 29725523 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional modulation of glutamatergic synaptic transmission by metabotropic glutamate type 7 receptors at Schaffer collateral-CA1 hippocampal synapses.J Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;596(5):921-940. doi: 10.1113/JP275371. Epub 2018 Jan 25. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29280494 Free PMC article.
-
Epac: new emerging cAMP-binding protein.BMB Rep. 2021 Mar;54(3):149-156. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.3.233. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 33298248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol drives aversive conditioning through dopamine 1 receptor and glutamate receptor-mediated activation of lateral habenula neurons.Addict Biol. 2017 Jan;22(1):103-116. doi: 10.1111/adb.12298. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26283508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weisskopf M. G., Castillo P. E., Zalutsky R. A., Nicoll R. A. (1994) Mediation of hippocampal mossy fiber long-term potentiation by cyclic AMP. Science 265, 1878–1882 - PubMed
-
- Herrero I., Sánchez-Prieto J. (1996) cAMP-dependent facilitation of glutamate release by β-adrenergic receptors in cerebrocortical nerve terminals. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 30554–30560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

