Two new sphingolipids from the leaves of Piper betle L
- PMID: 24036513
- PMCID: PMC6270174
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules180911241
Two new sphingolipids from the leaves of Piper betle L
Abstract
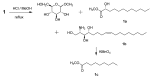
Two new sphingolipids, pipercerebrosides A (1) and B (2), were isolated from the leaves of Piper betle L. Their structures, including absolute configurations, were determined by spectroscopic analysis and chemical degradation. These two compounds did not show significant cytotoxic activity against the cancer cell lines K562 and HL-60 in a MTT assay.
Figures
References
-
- Wu Z.Y. Flora of China. Volume 20. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1982. Piper betle; pp. 42–45.
-
- Nagori K., Singh M.K., Alexander A., Kumar T., Dewangan D., Badwaik H., Tripathi D.K. Piper betle L.:A review on its ethnobotany, phytochemistry, pharmacological profile and profiling by new hyphenated technique DART-MS (Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry) J. Pharm. Res. 2011;4:2991–2997.
-
- Rai M.P., Thilakchand K.R., Palatty P.L., Rao P., Rao S., Bhat H.P., Baliga M.S. Piper betel Linn (betel vine), the maligned Southeast Asian medicinal plant possesses cancer preventive effects: Time to reconsider the wronged opinion. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011;12:2149–2156. - PubMed
-
- Kumar N., Misra P., Dube A., Bhattacharya S., Dikshit M., Ranade S. Piper betle Linn. A maligned Pan—Asiatic plant with an array of pharmacological activities and prospects for drug discovery. Curr. Sci. 2010;99:922–931.
-
- Huang X.Z., Yin Y., Huang W.Q., Sun K.Z., Cheng C.M., Bai L., Dai Y. Studies on alkaloids and lignins from stems of Piper betle L. China J. Chin. Mat. Med. 2010;35:15–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources