DNA polymerase δ stalls on telomeric lagging strand templates independently from G-quadruplex formation
- PMID: 24038470
- PMCID: PMC3905856
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt813
DNA polymerase δ stalls on telomeric lagging strand templates independently from G-quadruplex formation
Abstract
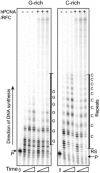
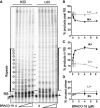
Previous evidence indicates that telomeres resemble common fragile sites and present a challenge for DNA replication. The precise impediments to replication fork progression at telomeric TTAGGG repeats are unknown, but are proposed to include G-quadruplexes (G4) on the G-rich strand. Here we examined DNA synthesis and progression by the replicative DNA polymerase δ/proliferating cell nuclear antigen/replication factor C complex on telomeric templates that mimic the leading C-rich and lagging G-rich strands. Increased polymerase stalling occurred on the G-rich template, compared with the C-rich and nontelomeric templates. Suppression of G4 formation by substituting Li(+) for K(+) as the cation, or by using templates with 7-deaza-G residues, did not alleviate Pol δ pause sites within the G residues. Furthermore, we provide evidence that G4 folding is less stable on single-stranded circular TTAGGG templates where ends are constrained, compared with linear oligonucleotides. Artificially stabilizing G4 structures on the circular templates with the G4 ligand BRACO-19 inhibited Pol δ progression into the G-rich repeats. Similar results were obtained for yeast and human Pol δ complexes. Our data indicate that G4 formation is not required for polymerase stalling on telomeric lagging strands and suggest that an alternative mechanism, in addition to stable G4s, contributes to replication stalling at telomeres.
Figures





References
-
- Palm W, de Lange T. How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008;42:301–334. - PubMed
-
- d'Adda di Fagagna F, Reaper PM, Clay-Farrace L, Fiegler H, Carr P, Von Zglinicki T, Saretzki G, Carter NP, Jackson SP. A DNA damage checkpoint response in telomere-initiated senescence. Nature. 2003;426:194–198. - PubMed
-
- Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW. Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature. 1990;345:458–460. - PubMed
-
- Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE. Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science. 1998;279:349–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

